WordPress のテンプレートとテンプレート階層について
WordPress のテンプレートとテンプレート階層について
更新日:2025年05月15日
作成日:2019年01月18日
テンプレート
テンプレートとは雛形のことで、ウェブページとして表示する情報をデータベースから取得し、ウェブページを生成する方法を制御する(WordPress のルールに従って記述された)PHP ファイルです。WordPress では、投稿などのデータベースに格納されたデータをテンプレート(ページの雛形)を使って出力・表示します。
テンプレートファイルは HTML、PHP、テンプレートタグで構成されています。
WordPress では、アクセスされたページに合わせて、表示するテンプレートファイルが自動的に選択されるようになっています。(テンプレートからページへの変換)
1つのテーマには複数のテンプレートを入れてページの種類によって使い分けることができます。テンプレートの名前(ファイル名)は WordPress が定めたルールがあり以下のようなテンプレートがあります(一部抜粋)。
| ページの種類 | テンプレート | 概要 |
|---|---|---|
| テーマの必須ファイル | index.php | 他に適切なテンプレートが存在しない場合に最終的に使用されるファイル(最も汎用的なテンプレート) |
| フロントページ | front-page.php | サイトのトップページを出力 |
| ホーム(メイン)ページ | home.php | ブログのトップページを出力 |
| 固定ページ | page.php | 個々の固定ページを出力 |
| 投稿 | single.php | 個々の投稿のページを出力 |
| カテゴリー | category.php | カテゴリーごとのアーカイブ(一覧)ページを出力 |
| タグ | tag.php | タグごとのアーカイブ(一覧)ページを出力 |
| 作成者 | author.php | 作成者別のアーカイブ(一覧)ページを出力 |
| 日付 | date.php | 日付ごとのアーカイブ(一覧)ページを出力 |
| アーカイブ | archive.php | アーカイブ(一覧)ページを出力 |
| 検索結果 | search.php | 検索結果のページを出力 |
| 404 (Not Found) | 404.php | 404エラー(Not Found)ページを出力 |
テンプレートには、優先順位が付いていて、WordPress はアクセスされたページによって優先順位の高いテンプレートを自動的に探します。
テンプレート階層
WordPress では、アクセスされた URL をもとに、各ページをテンプレートに基づいて出力します。その際に、複数のテンプレートの中から優先順位が高いものを選択する仕組みを「テンプレート階層(Template Hierarchy)」と呼びます。
WordPress Codex(日本語版):テンプレート階層
例えば、個々の投稿のページはテーマの中に single-post_type.php と言うテンプレートが含まれていれば、そのテンプレートを使って出力しますが、single-post_type.php がない場合は、single.php というテンプレートを使って出力します。single-post_type.php も single.php もなければ singular.php というテンプレートを使います(singular.php は Version 4.3 以降)。いずれのテンプレートもなければ、index.php を使って出力します。
以下はテンプレートファイルの優先順位を示す表です。左側ほど優先順位が高いテンプレートになります。
右側にあるほど優先順位は低くなり、逆に適用されるページの種類が多くなります。single-post_type.php は投稿専用のテンプレートですが、singular.php は投稿だけではなく、固定ページのテンプレートにも含まれます。もし、投稿と固定ページの構造がほぼ同じ場合、singular.php で投稿と固定ページの両方を出力するというようなことが可能です。
※テーマを作成する際は、テンプレート階層を理解して、作成するサイトの構造に合う適切なテンプレートを選択することがとても大切です。
| ページの種類 条件分岐タグ |
高い ← 優先度 → 低い | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| フロントページ is_front_page |
front-page.php | トップページ参照 | トップページ参照 | - | index.php | |
| ホームページ is_home |
home.php | - | - | - | ||
| カテゴリー is_category |
category-slug.php | category-id.php | category.php | archive.php | ||
| タグ is_tag |
tag-slug.php | tag-id.php | tag.php | |||
| カスタム分類 is_tax |
taxonomy-taxonomy-term.php | taxonomy-taxonomy.php | taxonomy.php | |||
| 作成者 is_author |
author-nicename.php | author-id.php | author.php | |||
| 日付 is_date,is_day is_month is_year |
date.php | - | - | |||
| アーカイブ is_archive is_post_type_archive |
archive-post_type.php | - | - | |||
| 検索結果 is_search |
search.php | - | - | - | ||
| 404 (Not Found) is_404 |
404.php | - | - | - | ||
| 固定ページ is_page is_singular |
customname.php (カスタムページテンプレート) |
page-slug.php | page-id.php | page.php |
singular.php ※ |
|
| 投稿/カスタム投稿 is_single is_singular |
single-post_type.php | - | - | single.php | ||
| 添付ファイル is_attachment is_singular |
MIME_type.php image.php video.php audio.php application.php |
attachment.php | single-attachment.php | |||
- オレンジ色の箇所は、id 名やスラッグ名、カスタム名の値を指定
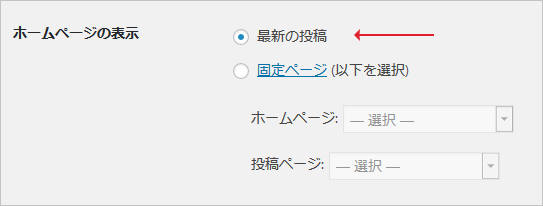
- フロントページ:特定のページをトップページに表示するときに使用。
「管理画面」→「設定」→「表示設定」の「ホームページの表示」で指定したページが表示される。「トップページのテンプレート」参照。 - ホームページ:Webサイトのトップページに使用。
「管理画面」→「設定」→「一般設定」の「サイトのアドレス(URL)」に設定されている URL にアクセスされた際に表示するページ。 - ※:Version 4.3 から新たに singular.php というテンプレートが追加されました。singular.phpは、固定ページ・投稿のテンプレートである page.php、single.php がない時に読み込まれます。
index.php
index.php は専用のテンプレートが存在しなかった場合に、最終的に選択されてそのページを出力する汎用的なテンプレートです。※ index.php はテーマに必須のテンプレートです。
例えば、トップページの表示には front-page.php が使われますが、存在しない場合は home.php が使われ、home.php も存在しない場合には、最終的に index.php が使われます。固定ページの page.php や投稿の single.php が存在しない場合にも、最終的に index.php が使われます。
つまり、index.php はあらゆる種類のテンプレートが存在しなかった場合に「最終的に使われる」テンプレートで、そのためテーマには必須になっています。
index.php は全てのページの最後の(優先順位の最も低い)テンプレートなので、index.php のテンプレートのみを使って出力するようなテーマも作成することは可能ですが、その場合、テンプレートのコード(条件分岐等)が複雑になる可能性があります。Web サイトの構造に合わせて、適切なテンプレートの設計が必要です。
また、テーマ内の index.php は通常の Web サイトのインデックスファイル(index.html など)に該当するデフォルトドキュメント(ファイル名を省略した場合にブラウザで表示されるファイル)ではありません。WordPress の場合、インデックスファイルは WordPress のインストールディレクトリにある index.php になります。
トップページのテンプレート
- front-page.php
- home.php
- index.php
- front-page.php が存在する場合は「管理画面」→「設定」→「表示設定」の「ホームページの表示」で「固定ページ」を選択している場合でも、front-page.php が優先される。(home.php、index.php に対しては固定ページが優先される)
- front-page.php と home.php の両方がある場合は front-page.php がトップページに表示される
- front-page.php と home.php がない場合は index.php がトップページに表示される
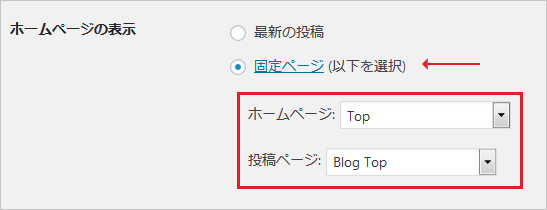
「ホームページの表示」で「固定ページ」を選択している場合、front-page.php や固定ページのテンプレートのメインループで取得できるのはその固定ページの記事になります。
「ホームページの表示」で「固定ページ」を選択している場合、front-page.php で投稿の一覧などを取得するには サブループ を利用します(pre_get_posts では条件分岐で is_front_page() が動作しません)。
関連項目:ホームページと投稿ページ
投稿のテンプレート
- single-{post_type(カスタム投稿名)}.php
- single.php
- singular.php
- index.php
- 通常の投稿記事の個別記事ページで使用するテンプレートは「single.php」
- スラッグや id で振り分けることはできないので、表示をページに合わせて分ける場合は条件分岐タグによる切り替えを行う
- (in_category などを使ってカテゴリーにより分岐し、get_template_part タグを利用してテンプレートパーツを読み込むなど)
- カスタム投稿を利用した場合は「single-カスタム投稿名.php(single-{post_type}.php)」のテンプレートで専用のテンプレートを利用できる
固定ページのテンプレート
- customname.php(カスタムテンプレートページ)
- page-slug.php
- page-id.php
- page.php(固定ページの汎用テンプレート)
- singular.php
- index.php
- 固定ページは、テンプレート階層でもっとも優先順位の高い「カスタムページテンプレート」を、ページごとに設定することができる。
WordPress Codex(日本語):固定ページ
カスタムページテンプレート
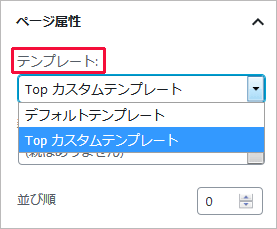
カスタムページテンプレート(カスタムテンプレート)は特定の「固定ページ」の生成に利用できるテンプレートで、任意のファイル名をつけて作成します。(カスタムページテンプレート)
テーマフォルダの中に、任意のファイル名のファイル(例:customname.php)を作成し、以下のようにページの先頭でコメントを使ってテンプレート名を指定します。(この名前は、管理画面「固定ページ」の編集画面のテンプレートのプルダウンに表示されます)
- ファイル名とテンプレート名が同一である必要はありません。
- Template Name: 「Template Name」と「:」の間にスペースを入れてはいけません。
- カスタムページテンプレートは複数のページで使用できます
<?php /* Template Name: テンプレート名(管理画面で表示されるテンプレート名:日本語可) */ ?> ここからは通常のテンプレートファイルと同じ
上記のコメントを追加したテンプレートファイルをテーマフォルダに保存すると、固定ページの新規追加・編集画面で「ページ属性」部分に「テンプレート」の項目が追加され、リストから識別名を選択すると、テンプレート階層より優先されるテンプレートファイルとして設定することができます。
カテゴリーページのテンプレート
- category-slug.php
- category-id.php
- category.php(カテゴリーの汎用テンプレート)
- archive.php(汎用アーカイブテンプレート。タグ・日別・アーカイブなどと共用)
- index.php
- カテゴリー記事の一覧などに使用するテンプレート
- すべてのカテゴリーを1つのデザインで表示する場合は、「category.php」のみで問題ないが、カテゴリーによりデザインを変更する場合は、条件分岐でデザインを変更するか、カテゴリーのスラッグや id を使用してテンプレートを分けることができる
WordPress Codex(日本語):カテゴリーテンプレート
タグ表示ページのテンプレート
- tag-slug.php
- tag-id.php
- tag.php(タグの汎用テンプレート)
- archive.php(汎用アーカイブテンプレート。カテゴリー・日別・アーカイブなどと共用)
- index.php
- タグとは関連記事をまとめたりする際の目印のような機能
- タグのスラッグや id を使用してテンプレートを分けることができる
カスタム分類のテンプレート
- taxonomy-{taxonomy}-{term}.php
カスタムタクソノミー名が「topicscat」、タームのスラッグが「economy」の場合:
taxonomy-topicscat-economy.php - taxonomy-{taxonomy}.php
カスタムタクソノミー名が「topicscat」の場合:
taxonomy-topicscat.php - taxonomy.php
- archive.php
- index.php
- ターム:カスタムタクソノミーで作成するタグ機能やカテゴリー機能を持ったもの
WordPress Codex(日本語):カスタム分類
カスタム投稿一覧表示のテンプレート
- archive-{post_type(カスタム投稿名)}.php
- archive.php(汎用アーカイブテンプレート。カテゴリー・タグ・日別・アーカイブなどと共用)
- カスタム投稿タイプのインデックスページ(一覧ページ)は archive-投稿タイプ名.php というテンプレートで扱うことができる。(3.1以降)
- カスタム投稿タイプのアーカイブを表示するためには、カスタム投稿タイプを登録のとき、register_post_type() の引数に、‘has_archive’ => true を指定する
カスタム投稿タイプのテンプレートは「投稿のテンプレート」を参照ください。
WordPress Codex(日本語):カスタム投稿タイプ(投稿タイプ)
関連ページ:カスタム投稿タイプの一覧を表示
日付表示テンプレート
- date.php
- archive.php
- index.php
- ブログなどで日時別の一覧を表示するときに使用する。
- 通常サイトでは更新情報の一覧を年/月ごとに表示する場合などに使用。
404 テンプレート
- 404.php
- index.php
404 エラーの際に表示するページのテンプレート。
WordPress では該当するページが見つからなかった場合(URL の解析でページ種類が決定しなかった場合)、404.php を呼び出すようになっています。
但し、404.php が存在しない場合は index.php が表示されてしまいます。
テーマには 404.php(404 ページ)を作成して適切なエラーメッセージなどを表示するようにします。
テンプレートからページへの変換
HTML で作成した静的な Web サイトの場合、ファイルの物理的な位置が URL と関連しますが、WordPress の場合は異なります。
WordPress の場合、テーマに必須の index.php さえあれば、どのような URL でも(トップページや投稿、固定ページ、カテゴリーページなど)表示させることができ、各ページをそれぞれのファイルで表示する静的なサイトとは構造が違っています。
アクセスされたページ(リクエストされた URL)をどのテンプレートで表示するかは以下のような仕組みになっています。
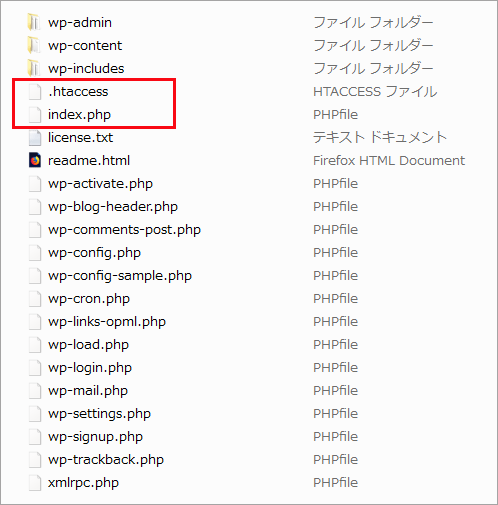
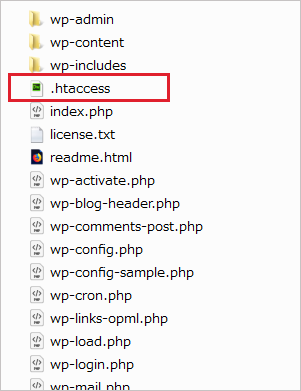
WordPress をインストールしたディレクトリを見ると、以下のように .htaccess 及び index.php と言うファイルがあります。
以下は WordPress を wp と言うディレクトリにインストールした場合に生成される、.htaccess の例です。
# BEGIN WordPress
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c> #mod_rewrite が使用できる場合
RewriteEngine On #mod_rewrite の機能を有効に
RewriteBase /wp/ #Rewrite 処理のベースとなる URL の指定
RewriteRule ^index\.php$ - [L] #ファイル名が index.php なら処理を終了
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f #指定したファイルが存在しなければ
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d #且つ指定したディレクトリが存在しなければ
RewriteRule . /wp/index.php [L] #すべてのリクエスト(.)は /wp/index.php に書き換え
</IfModule>
# END WordPress
内容は「リクエストされたファイルが存在せず(6行目)」かつ「リクエストされたディレクトリが存在しない(7行目)」場合はどんなファイル(.)でも /wp/index.php へ書き換える(8行目)と言うような指示が記述されています( .htaccess )。
つまり、指定されたファイルやディレクトリがない場合は、インストールディレクトリの index.php を参照するようにとなっています。
インストールディレクトリの index.php
以下がインストールディレクトリにある index.php に記述されている内容です。冒頭のコメントには「WordPress アプリケーションへの入り口です。このファイルはテーマをロードするために wp-blog-header.php を読み込む(load)以外は何もしません。」というようなことが記述されています。
define('WP_USE_THEMES', true) は、define() 関数でテーマファイルを読み込むかどうかの定数「WP_USE_THEMES」を「true」に定義しています。後述する「③ テーマのテンプレートのロード(wp-include/template-loader.php)」でこの定数を使ってテーマのテンプレートを読み込むかどうか条件分岐しています。
require() は外部ファイルを読み込む指示で、dirname() はディレクトリのパスを返してくれる関数です。
dirname( __FILE__ ) は、そのファイルのあるディレクトリのパスを返してくれるので、同じディレクトリ(インストールディレクトリ)にある wp-blog-header.php を読み込む指示になります。
<?php /* index.php */
/**
* Front to the WordPress application. This file doesn't do anything, but loads
* wp-blog-header.php which does and tells WordPress to load the theme.
*/
/**
* Tells WordPress to load the WordPress theme and output it.
* @var bool
*/
define('WP_USE_THEMES', true);
/** Loads the WordPress Environment and Template */
require( dirname( __FILE__ ) . '/wp-blog-header.php' );
wp-blog-header.php
Codex 日本語版の WP_Query クラスの説明には「wp-blog-header.php が $wp_query オブジェクトに現在のリクエストを定義する情報を与えることで、$wp_query はどのタイプのクエリを扱っているのかを確定し、要求された投稿を取り出します。」とあります。
この辺の部分に「WordPress がリクエストされた URL を元にそのページに必要なデータを自動的に用意する」仕組みが記述されています。
同じディレクトリ(インストールディレクトリ)にある wp-blog-header.php を見ると以下のようになっています。
コメントには「WordPress の環境設定とテンプレートを読み込む」とあります。
<?php /* wp-blog-header.php */
/**
* Loads the WordPress environment and template.
* @package WordPress
*/
if ( !isset($wp_did_header) ) {
$wp_did_header = true;
// ① Load the WordPress library.
require_once( dirname(__FILE__) . '/wp-load.php' );
// ② Set up the WordPress query.
wp();
// ③ Load the theme template.
require_once( ABSPATH . WPINC . '/template-loader.php' );
}
① WordPress のライブラリの読み込み
require_once( dirname(__FILE__) . '/wp-load.php' );
wp-load.php では、定数(ABSPATH)の定義や設定ファイル(wp-config.php)の読み込みなどが行われます。
/* wp-load.php 抜粋*/ define( 'ABSPATH', dirname( __FILE__ ) . '/' ); require_once( ABSPATH . 'wp-config.php' );
wp-config.php には、WordPress をインストールした際に入力したデータベースへの接続情報などの設定情報が保存されています。また、wp-settings.php の読み込みも記述されています。
/* wp-config.php 一部抜粋 */
/** WordPress のためのデータベース名 */
define('DB_NAME', 'database_name_here');
/** MySQL データベースのユーザー名 */
define('DB_USER', 'username_here');
/** MySQL データベースのパスワード */
define('DB_PASSWORD', 'password_here');
/** MySQL のホスト名 */
define('DB_HOST', 'localhost');
/** データベースのテーブルを作成する際のデータベースの文字セット */
define('DB_CHARSET', 'utf8');
/** データベースの照合順序 (ほとんどの場合変更する必要はありません) */
define('DB_COLLATE', '');
/** Sets up WordPress vars and included files. */
require_once(ABSPATH . 'wp-settings.php');
wp-settings.php には、必要なファイルの読み込みやデフォルトのフィルター、テーマの functions.php の読み込み、$wp_query の生成、init、wp_loaded、setup_theme、after_setup_theme などのアクションフックの実行なども記述されています。
//wp-settings.php(抜粋)
/**
* Used to set up and fix common variables and include
* the WordPress procedural and class library.
* Allows for some configuration in wp-config.php (see default-constants.php)
* @package WordPress
* Stores the location of the WordPress directory of functions,classes,and core content.
* @since 1.0.0
*/
define( 'WPINC', 'wp-includes' );
// Include files required for initialization.
require( ABSPATH . WPINC . '/load.php' );
require( ABSPATH . WPINC . '/default-constants.php' );
require_once( ABSPATH . WPINC . '/plugin.php' );
・・・中略・・・
// Load early WordPress files.
require( ABSPATH . WPINC . '/compat.php' );
require( ABSPATH . WPINC . '/class-wp-list-util.php' );
require( ABSPATH . WPINC . '/functions.php' );
require( ABSPATH . WPINC . '/class-wp-matchesmapregex.php' );
require( ABSPATH . WPINC . '/class-wp.php' );
require( ABSPATH . WPINC . '/class-wp-error.php' );
require( ABSPATH . WPINC . '/pomo/mo.php' );
// Include the wpdb class and, if present, a db.php database drop-in.
global $wpdb;
require_wp_db();
// Set the database table prefix and the format specifiers for database table columns.
$GLOBALS['table_prefix'] = $table_prefix;
wp_set_wpdb_vars();
// Start the WordPress object cache, or an external object cache if the drop-in is present.
wp_start_object_cache();
// Attach the default filters.(デフォルトフィルタの読み込み)
require( ABSPATH . WPINC . '/default-filters.php' );
・・・中略・・・
// Load most of WordPress.(wp-includes にあるほとんどのファイルの読み込み)
require( ABSPATH . WPINC . '/class-wp-walker.php' );
require( ABSPATH . WPINC . '/class-wp-ajax-response.php' );
require( ABSPATH . WPINC . '/formatting.php' );
require( ABSPATH . WPINC . '/capabilities.php' );
・・・
・・・中略・・・
/* Fires once all must-use and network-activated plugins have loaded. */
do_action( 'muplugins_loaded' );
・・・
/* Fires once activated plugins have loaded. */
do_action( 'plugins_loaded' );
・・・
/**
* WordPress Query object
*
* @global WP_Query $wp_the_query
* @since 2.0.0
*/
$GLOBALS['wp_the_query'] = new WP_Query();
//$wp_the_query オブジェクト(WP_Queryクラスのインスタンス)の生成
//スーパーグローバル変数 $GROBALS に格納
/**
* Holds the reference to @see $wp_the_query
* Use this global for WordPress queries
*
* @global WP_Query $wp_query
* @since 1.5.0
*/
$GLOBALS['wp_query'] = $GLOBALS['wp_the_query'];
//$wp_query オブジェクトに $wp_the_query オブジェクトをコピー
//$GLOBALS['wp_the_query'] は $GLOBALS['wp_query']のバックアップ
/**
* Holds the WordPress Rewrite object for creating pretty URLs
*
* @global WP_Rewrite $wp_rewrite
* @since 1.5.0
*/
$GLOBALS['wp_rewrite'] = new WP_Rewrite();
/**
* WordPress Object
*
* @global WP $wp
* @since 2.0.0
*/
$GLOBALS['wp'] = new WP();
・・・
/* Fires before the theme is loaded. */
do_action( 'setup_theme' );
・・・
//Load the functions for the active theme,for both parent and child theme if applicable.(テーマの functions.php の読み込み)
if ( ! wp_installing() || 'wp-activate.php' === $pagenow ) {
if ( TEMPLATEPATH !== STYLESHEETPATH && file_exists( STYLESHEETPATH . '/functions.php' ) )
include( STYLESHEETPATH . '/functions.php' );
if ( file_exists( TEMPLATEPATH . '/functions.php' ) )
include( TEMPLATEPATH . '/functions.php' );
}
/* Fires after the theme is loaded */
do_action( 'after_setup_theme' );
・・・
/*
Fires after WordPress has finished loading but before any headers are sent.
Most of WP is loaded at this stage, and the user is authenticated.
WP continues to load on the {@see 'init'} hook that follows (e.g. widgets), and many plugins instantiate themselves on it for all sorts of reasons (e.g. they need a user, a taxonomy, etc.).
If you wish to plug an action once WP is loaded, use the {@see 'wp_loaded'} hook below.
*/
do_action( 'init' );
・・・
/* This hook is fired once WP, all plugins, and the theme are fully loaded and instantiated. */
do_action( 'wp_loaded' );
② WordPress クエリのセットアップ
wp();
wp() 関数の実行。アクセスされた URL を元にクエリー条件の設定や、アクセスされた URL に該当するページのデータをデータベースからの読み込みを実行(グローバル変数 $posts にデータベースの情報が設定される)。
以下は wp() の定義で、$wp->main() が呼び出されています(wp-include/functions.php)。
function wp( $query_vars = '' ) {
global $wp, $wp_query, $wp_the_query; //$wp、$wp_query、$wp_the_query を関数内で使用するためのグローバル宣言
$wp->main( $query_vars );
if ( !isset($wp_the_query) )
$wp_the_query = $wp_query;
//$wp_the_query がまだ設定されていなければ $wp_query を代入(コピー作成=バックアップ)
}
main() は wp-include/class-wp.php に以下のように定義されていて、「リクエストに基づくクエリ変数のセットアップ」「クエリ変数に基づくループをセットアップ」「リクエストされた URL が見つからない場合 404ヘッダをセット」「グローバル変数のセットアップ」「wp アクションフックの実行」などが行われています。
//class WP
public function main($query_args = '') {
$this->init(); //現在のユーザーをセットアップ(Set up the current user)
$this->parse_request($query_args); //リクエストに基づくクエリ変数のセットアップ(Sets up the query variables based on the request)
$this->send_headers(); //追加の HTTP ヘッダを送信(Sends additional HTTP headers for caching, content type, etc)
$this->query_posts(); //クエリ変数に基づくループをセットアップ(Set up the Loop based on the query variables)
$this->handle_404(); //リクエストされた URL が見つからない場合 404ヘッダをセット
$this->register_globals(); //グローバル変数のセットアップ
/**
* Fires once the WordPress environment has been set up.
*
* @since 2.1.0
*
* @param WP $this Current WordPress environment instance (passed by reference).
*/
do_action_ref_array( 'wp', array( &$this ) ); //wp アクションフックの実行
}
「リクエストに基づくクエリ変数のセットアップ」
上記の main() の定義の4行目の parse_request() でリクエストに基づいてクエリ変数をセットアップしています。言い換えると、正しいクエリを取得すためにリクエストを解析しています。このメソッドには結果のクエリ変数を変更するためのたくさんのフィルターやアクションが含まれています。
「クエリ変数に基づくループをセットアップ」
上記の main() の定義の6行目 $this->query_posts() の query_posts() は wp-includes/class-wp.php で以下のように定義されています。
//class WP
/**
* Set up the Loop based on the query variables.
* クエリ変数に基づくループをセットアップ
* @since 2.0.0
*
* @global WP_Query $wp_the_query
*/
public function query_posts() {
global $wp_the_query; //$wp_the_query を関数内で使用するためのグローバル宣言
$this->build_query_string();
$wp_the_query->query( $this->query_vars );
}
build_query_string() は wp-include/class-wp.php に以下のように定義されていて、query_vars から query_string(クエリ文字列)を生成して、parse_str() で query_vars に格納しているようです。
//class WP
/**
* Sets the query string property based off of the query variable property.
*
* The {@see 'query_string'} filter is deprecated, but still works. Plugins should
* use the {@see 'request'} filter instead.
*
* @since 2.0.0
*/
public function build_query_string() {
$this->query_string = '';
foreach ( (array) array_keys( $this->query_vars ) as $wpvar ) {
if ( '' != $this->query_vars[ $wpvar ] ) {
$this->query_string .= ( strlen( $this->query_string ) < 1 ) ? '' : '&';
if ( ! is_scalar( $this->query_vars[ $wpvar ] ) ) { // Discard non-scalars.
continue;
}
$this->query_string .= $wpvar . '=' . rawurlencode( $this->query_vars[ $wpvar ] );
}
}
if ( has_filter( 'query_string' ) ) { // Don't bother filtering and parsing if no plugins are hooked in.
/**
* Filters the query string before parsing.
*
* @since 1.5.0
* @deprecated 2.1.0 Use 'query_vars' or 'request' filters instead.
*
* @param string $query_string The query string to modify.
*/
$this->query_string = apply_filters( 'query_string', $this->query_string );
parse_str( $this->query_string, $this->query_vars );
}
}
query_posts() 定義での $wp_the_query は $wp_query の元になる WP_Query クラスのインスタンスです。そのメソッド query() は wp-includes/class-wp-query.php で以下のように定義されています。
//class WP_Query
/**
* Sets up the WordPress query by parsing query string.
* クエリ文字列を解析して WordPress のクエリをセットアップ
* @since 1.5.0
*
* @param string|array $query URL query string or array of query arguments.
* @return WP_Post[]|int[] Array of post objects or post IDs.
*/
public function query( $query ) {
$this->init();
$this->query = $this->query_vars = wp_parse_args( $query );
return $this->get_posts();
}
init() は、以下のように定義されていてオブジェクトのプロパティ($posts, $queried_object, $post など)を初期化したりデフォルト値を設定しています。(wp-includes/class-wp-query.php)
//class WP_Query
/**
* Initiates object properties and sets default values.
*
* @since 1.5.0
*/
public function init() {
unset( $this->posts );
unset( $this->query );
$this->query_vars = array();
unset( $this->queried_object );
unset( $this->queried_object_id );
$this->post_count = 0;
$this->current_post = -1;
$this->in_the_loop = false;
unset( $this->request );
unset( $this->post );
unset( $this->comments );
unset( $this->comment );
$this->comment_count = 0;
$this->current_comment = -1;
$this->found_posts = 0;
$this->max_num_pages = 0;
$this->max_num_comment_pages = 0;
$this->init_query_flags();
}
$this->query = $this->query_vars = wp_parse_args( $query ); の wp_parse_args() は引数($query: URL のクエリ文字列またはクエリ引数)の連想配列を返します。
$this->get_posts() は1400行以上のとても長いメソッドで、クエリ変数に基づいて取得した投稿のオブジェクトの配列(an array of posts)を返しています。このメソッドの実行でグローバル変数 $posts にデータベースからの情報がセットアップされているようです。
以下は wp-includes/class-wp-query.php に定義されているメソッド get_posts() の最初と最後の部分の抜粋です。先頭の方で pre_get_posts のアクションフックの実行の記述があります。
//class WP_Query
/**
* Retrieves an array of posts based on query variables.
* クエリ変数に基づいた投稿のオブジェクトの配列を取得
*
* There are a few filters and actions that can be used to modify the post database query.
*
* @since 1.5.0
*
* @return WP_Post[]|int[] Array of post objects or post IDs.
*/
public function get_posts() {
global $wpdb;
$this->parse_query();
/**
* Fires after the query variable object is created, but before the actual query is run.
*
* Note: If using conditional tags, use the method versions within the passed instance
* (e.g. $this->is_main_query() instead of is_main_query()). This is because the functions
* like is_main_query() test against the global $wp_query instance, not the passed one.
*
* @since 2.0.0
*
* @param WP_Query $this The WP_Query instance (passed by reference).
*/
do_action_ref_array( 'pre_get_posts', array( &$this ) );
// Shorthand.
$q = &$this->query_vars;
// Fill again in case pre_get_posts unset some vars.
$q = $this->fill_query_vars( $q );
// Parse meta query
$this->meta_query = new WP_Meta_Query();
$this->meta_query->parse_query_vars( $q );
・・・中略・・・
・・・中略・・・
・・・中略・・・
// Ensure that any posts added/modified via one of the filters above are
// of the type WP_Post and are filtered.
if ( $this->posts ) {
$this->post_count = count( $this->posts );
$this->posts = array_map( 'get_post', $this->posts );
if ( $q['cache_results'] ) {
update_post_caches( $this->posts, $post_type, $q['update_post_term_cache'], $q['update_post_meta_cache'] );
}
$this->post = reset( $this->posts );
} else {
$this->post_count = 0;
$this->posts = array();
}
if ( $q['lazy_load_term_meta'] ) {
wp_queue_posts_for_term_meta_lazyload( $this->posts );
}
return $this->posts;
}
「グローバル変数のセットアップ」
以下は wp-includes/class-wp.phpp に定義されているメソッド register_globals() です。$wp_query の query_vars を使ってグローバル変数をセットアップしています。
//class WP
/**
* Set up the WordPress Globals.
*
* The query_vars property will be extracted to the GLOBALS. So care should
* be taken when naming global variables that might interfere with the
* WordPress environment.
*
* @since 2.0.0
*
* @global WP_Query $wp_query
* @global string $query_string Query string for the loop.
* @global array $posts The found posts.
* @global WP_Post|null $post The current post, if available.
* @global string $request The SQL statement for the request.
* @global int $more Only set, if single page or post.
* @global int $single If single page or post. Only set, if single page or post.
* @global WP_User $authordata Only set, if author archive.
*/
public function register_globals() {
global $wp_query;
// Extract updated query vars back into global namespace.
foreach ( (array) $wp_query->query_vars as $key => $value ) {
$GLOBALS[ $key ] = $value;
}
$GLOBALS['query_string'] = $this->query_string;
$GLOBALS['posts'] = & $wp_query->posts;
$GLOBALS['post'] = isset( $wp_query->post ) ? $wp_query->post : null;
$GLOBALS['request'] = $wp_query->request;
if ( $wp_query->is_single() || $wp_query->is_page() ) {
$GLOBALS['more'] = 1;
$GLOBALS['single'] = 1;
}
if ( $wp_query->is_author() && isset( $wp_query->post ) ) {
$GLOBALS['authordata'] = get_userdata( $wp_query->post->post_author );
}
}
③ テーマのテンプレートの読み込み
require_once( ABSPATH . WPINC . '/template-loader.php' );
ABSPATH は絶対パスを表す定数で、WPINC は wp-include フォルダを意味します。
wp-include フォルダにある template-loader.php(テンプレートの読み込み)は以下のようになっています。
どのテンプレートを読み込むかを決定する前に、template_redirect アクションが実行され、その後読み込むテンプレートを決定しています。
/* template-loader.php 一部抜粋 */
/**
* Loads the correct template based on the visitor's url
* リクエストされた URL を基に適切なテンプレートを読み込む
*/
if ( wp_using_themes() ) {
/**
* Fires before determining which template to load.
* どのテンプレートを使うかを振り分ける前に template_redirect アクションを実行
*/
do_action( 'template_redirect' );
}
・・・中略・・・
if ( wp_using_themes() ) :
$template = false;
if ( is_embed() && $template = get_embed_template() ) :
elseif ( is_404() && $template = get_404_template() ) :
elseif ( is_search() && $template = get_search_template() ) :
elseif ( is_front_page() && $template = get_front_page_template() ) :
elseif ( is_home() && $template = get_home_template() ) :
elseif ( is_privacy_policy() && $template = get_privacy_policy_template() ) :
elseif ( is_post_type_archive() && $template = get_post_type_archive_template() ) :
elseif ( is_tax() && $template = get_taxonomy_template() ) :
elseif ( is_attachment() && $template = get_attachment_template() ) :
remove_filter( 'the_content', 'prepend_attachment' );
elseif ( is_single() && $template = get_single_template() ) :
elseif ( is_page() && $template = get_page_template() ) :
elseif ( is_singular() && $template = get_singular_template() ) :
elseif ( is_category() && $template = get_category_template() ) :
elseif ( is_tag() && $template = get_tag_template() ) :
elseif ( is_author() && $template = get_author_template() ) :
elseif ( is_date() && $template = get_date_template() ) :
elseif ( is_archive() && $template = get_archive_template() ) :
else :
$template = get_index_template();
endif;
・・・以下省略・・・
template-loader.php は、is_single() や is_page() などの条件分岐タグと get_single_template() などのテンプレートのパスを取得する関数を使って、HTML を生成するためのテンプレートを決定しています。
言い換えると、アクセスされたページ(リクエストされた URL)をどのテンプレートで表示するかと言うテンプレート階層の仕組みが記述されています。
WordPress は上記のような手順でアクセスされたページに該当するテンプレートを探します。もし、どのテンプレートにも該当しない場合は、最後の get_index_template() が実行され、index.php が読み込まれます。
ファイルの読み込み順序
以下がファイルの読み込みの概要です。
- インストールディレクトリの index.php(wp-blog-header.php の読み込み)
- wp-blog-header.php(wp-load.php の読み込み)
- wp-load.php(wp-config.php の読み込み)
- wp-config.php(データベースへの接続情報などの読み込みや wp-settings.php の読み込み)
- wp-settings.php($wp_query の生成、functions.php や各種設定ファイルの読み込み、init、wp_loaded、setup_theme、after_setup_theme アクションフックの実行 などを含む設定情報の読み込み)
wp() 関数の実行。アクセスされた URL を元にクエリー条件の設定(query_var や query_string)、該当するページのデータのデータベースからの読み込み(グローバル変数 $posts にデータベースの情報を設定)、404の設定。 - template-loader.php テーマのテンプレートの読み込み(アクセスされたページ、つまりリクエストされた URL をどのテンプレートで表示するかを決定)
※テーマのテンプレートが読み込まれる時点では、すでにそのページのデータはリクエストされた URL を元に WordPress がデータベースから自動的に取得(1~5)されています。
関連情報参考ページ
テンプレートパーツ
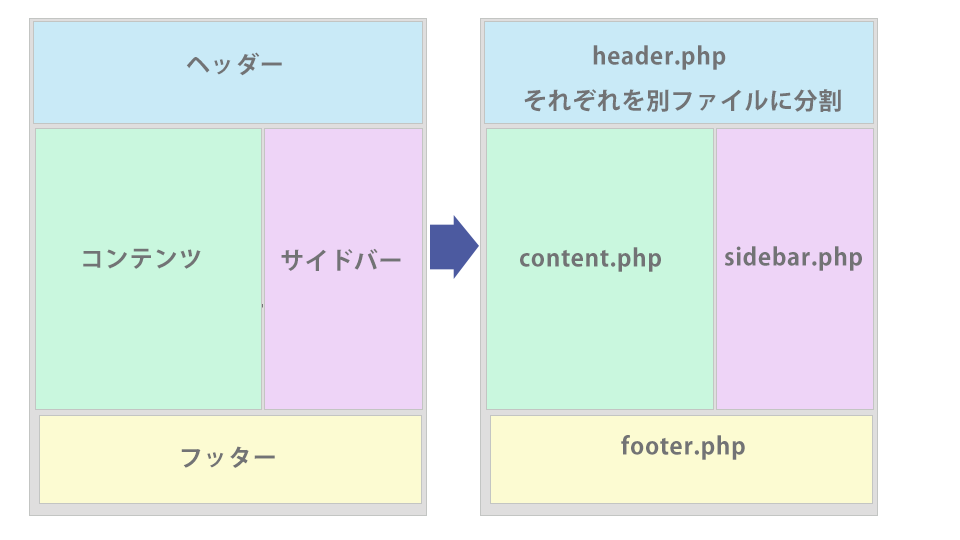
一般的な Web サイトの構造は、ヘッダー、コンテンツ部分、サイドバー、フッターなどから構成されています。ページごとにテンプレートを作成していくと、ヘッダーやフッターなどの共通部分を繰り返し記述することになるので、共通のパーツは「テンプレートパーツ」と言うテンプレートファイルに記述して、各テンプレートでインクルードタグを使って読み込みます。
テンプレートパーツは「パーツテンプレート」や「モジュールテンプレート」、または単にテンプレートと呼ばれることもあり、テンプレートを構成するファイルのことです。
| パーツ | テンプレートファイル名 | 読み込むためのインクルードタグ |
|---|---|---|
| ヘッダー | header.php | <?php get_header(); ?> |
| header-{name}.php | <?php get_header($name); ?> | |
| フッター | footer.php | <?php get_footer(); ?> |
| footer-{name}.php | <?php get_footer($name); ?> | |
| サイドバー | sidebar.php | <?php get_sidebar(); ?> |
| sidebar-{name}.php | <?php get_sidebar($name); ?> | |
| 検索フォーム | searchform.php | <?php get_search_form(); ?> |
| コメント | comments.php | <?php comments_template(); ?> |
| カスタム | aaa.php | <?php get_template_part('aaa'); ?> |
| aaa-bbb.php | <?php get_template_part('aaa', 'bbb'); ?> |
それぞれのインクルードタグについては「テンプレートの読み込みを行う関数」を参照ください。
404 ページ
WordPress ではパーマリンクの設定を元に URL が解析されてページ種類が決定されます。
もし、URL の解析でページ種類が決定しなかった場合は 404.php と言うテンプレートファイルが呼び出されるようになっています。
但し、WordPress では該当するページがない場合、優先的に index.php が表示されるようになっているため、404.php が存在しない場合は index.php が表示されます。
このため、テーマには 404.php を作成して適切なエラーメッセージを表示します。
※静的な HTML を使ったサイトで「ファイルが存在しない」時に 404 エラーになるのとは仕組みが異なります。
また、404 ページが表示されているかどうかは is_404() 条件分岐タグで判定することができます。
404エラーページの作成
WordPress の場合、404エラーページは 404.php と言うテンプレートファイルを作成してテーマディレクトリに配置します。
404 ページを作成する場合には以下のようなことを考慮します(Search Console ヘルプ:404 ページのカスタマイズ から引用)。
- ユーザーに対して、探しているページが見つからないことを明確に伝える。
- 404 ページを、サイトのその他の部分と同じデザイン(ナビゲーションを含む)にする。
- 最も人気のある記事や投稿へのリンクの他、ホームページへのリンクなどを追加する。
- 404 ページが検索エンジンのインデックスに登録されないようにするため、存在しないページがリクエストされたときにウェブサーバーが実際の 404 HTTP ステータス コードを返すことを確認する。
以下は 404.php の例です。
<!-- 404.php -->
<?php get_header(); ?>
<div id="main">
<h2>404 Not Found(ページが見つかりませんでした)</h2>
<p><img src="<?php echo get_theme_file_uri('/images/error_message.png'); ?>" alt="エラーメッセージの画像"></p>
<p>指定された以下のページは存在しないか、または移動した可能性があります。</p>
<p class="error_url">URL :<span><?php echo get_pagenum_link(); ?></span></p>
<p>現在表示する記事がありません。よろしければ、検索ボックスにお探しのコンテンツに該当するキーワードを入力して下さい。</p>
<?php get_search_form(); ?><!-- 検索フォームを表示 -->
<p><a href="<?php echo home_url(); ?>">トップページへ</a></p>
</div>
<?php
get_sidebar();
get_footer();
リクエストされたページの URL は get_pagenum_link() で取得しています。get_pagenum_link() は指定されたページ番号のリンクを取得しますが、ページ番号を指定しなければ現在のページの URL が取得できます。また取得する値はデフォルトで esc_url() によりエスケープ処理されています。
以下のように $_SERVER 変数を使って記述しても表示できます。
<?php $protocol = empty($_SERVER["HTTPS"]) ? "http://" : "https://"; echo esc_url($protocol. $_SERVER["HTTP_HOST"].$_SERVER["REQUEST_URI"]); ?>
または1行にまとめると以下のようになります。
<?php echo esc_url((empty($_SERVER['HTTPS']) ? "http://" : "https://") . $_SERVER["HTTP_HOST"] . $_SERVER["REQUEST_URI"]); ?>
検索フォームの表示は get_search_form() を使ってデフォルトの検索フォームを表示しています。
以下は公式テーマ twentynineteen の 404.php です。ページが見つからなかったと言う内容のメッセージを表示して、検索フォームを表示しています。
<!-- twentynineteen 404.php -->
<?php get_header(); ?>
<section id="primary" class="content-area">
<main id="main" class="site-main">
<div class="error-404 not-found">
<header class="page-header">
<h1 class="page-title"><?php _e( 'Oops! That page can’t be found.', 'twentynineteen' ); ?></h1>
</header><!-- .page-header -->
<div class="page-content">
<p><?php _e( 'It looks like nothing was found at this location. Maybe try a search?', 'twentynineteen' ); ?></p>
<?php get_search_form(); ?>
</div><!-- .page-content -->
</div><!-- .error-404 -->
</main><!-- #main -->
</section><!-- #primary -->
<?php
get_footer();
404 HTTP ステータスコードの確認
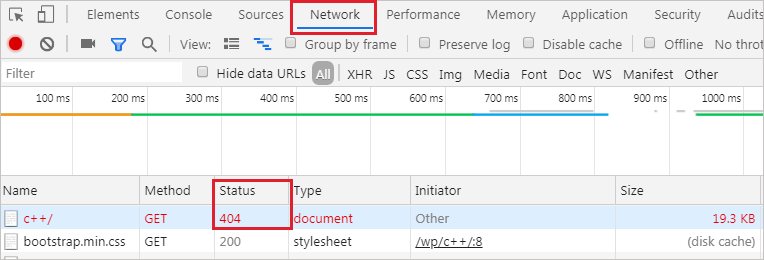
WordPress で 404.php ファイルを作成して、そのファイルが読み出される際には自動的に 404 HTTP ステータスコードが返されるようになっていますが、念のためブラウザのネットワークツールなどで確認します。
Windows の場合、Chrome や Firefox では F12 キーを押して「ネットワーク」を選択して確認することができます。
エラーが出ても 404.php でページが生成されない場合
エラーが出ても 404.php でページが生成されない場合は、WordPress をインストールしたディレクトリの .htaccess に「ErrorDocument 404 /index.php?error=404」という設定を追加します。
# BEGIN WordPress
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteRule ^index\.php$ - [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule . /wp/index.php [L]
</IfModule>
# END WordPress
ErrorDocument 404 /index.php?error=404
WordPress をサブディレクトリにインストールしている場合は、「ErrorDocument 404 /サブディレクトリ名/index.php?error=404」という形で指定する必要があります。
ErrorDocument 404 /サブディレクトリ名/index.php?error=404
.htaccess ファイルは Wordpress をインストールしたディレクトリに自動的に生成されます。
必要のないページ種類の場合に404を表示する方法
WordPress はページ種類の制御を URL で行っているため、存在しないけれどパーマリンク設定に従った URL を入力すると関係のないページが表示される場合があります。
このような動作を防ぐために使用しているページの種類以外の場合に、template_redirect フックを使って 404 を表示するように指定することもできます。
但し、この方法の場合、サイトに新たなページ種類を追加した場合にはそれらのページも 404 になってしまうので記述を更新する必要があります。
以下は if 文で指定した以下のページ種類以外の場合 404 ページにリダイレクトさせる例です。
- ホームページ
- 個別ページ(投稿、カスタム投稿タイプ、添付ファイル及び固定ページ)
- 月別アーカイブページ
- カテゴリーページ
- タグページ
- rental と言うカスタム投稿タイプのページ
- 検索結果ページ
以下の場合、カスタムタクソノミーやフィードなどの以下で指定していないページでは 404 エラーになります。
function redirect_404() {
//以下のページ種類以外の指定の場合 404 ページを表示する
if(is_home() || is_singular() || is_month() || is_category() || is_tag() || is_post_type_archive('rental') || is_search()) return;
//HTTP ステータスコード 404 を送信
status_header(404);
include TEMPLATEPATH . '/404.php';
exit(); //または die(); を使ってこれ以上リダイレクトさせない
}
add_action('template_redirect', 'redirect_404');
TEMPLATEPATH は現在の(親)テーマのディレクトリへのパスが格納されています。get_template_directory() で取得する値と同じです。
関連ページ:404 ページの作成
Codex 日本語版:404エラーページの作成