TypeScript 環境の構築
TypeScript は JavaScript に「静的型付け」を追加したプログラミング言語で、JavaScript の使える場面では代わりに TypeScript を使うことができます。
但し、ブラウザや Node.js は TypeScript のコードをそのままでは解釈できないので、TypeScript を JavaScript にコンパイルする必要があります。
以下は TypeScript を利用するための環境を構築する手順や TypeScript を直接 Node.js で実行するためのツール tsx(TypeScript Execute)、esbuild-register、ts-node、nodemon、ts-node-dev などの使い方、プロジェクトを ES Modules に(Native ESM)する方法などについての解説のような覚書です。
作成日:2023年2月1日
関連ページ
- TypeScript を使ってみる(基本型や型注釈)
- TypeScript 関数
- TypeScript クラス
- TypeScript 高度な型
- TypeScript モジュール
- TypeScript で Promise や Async/Await(非同期処理)
TypeScript の開発環境
以下では Node.js のパッケージ管理ツール npm(Node Package Manager)を使用します。
npm は Node.js をインストールすると自動的にインストールされます。以降では Node.js がすでにインストールされていることを前提にしています。
Node.js のインストール方法や npm の使い方は以下に掲載していますのでよろしければ御覧ください。
以下をコマンドライン上で実行してバージョンが表示されれば、Node.js と npm がインストールされています。以下は Mac のターミナルの例で、% はプロンプトの表示です(% は入力はしません)。
% node -v return v20.6.1 // Node.js のバージョン % npm -v return 10.1.0 // npm のバージョン
また、使用するエディタは TypeScript をデフォルトでサポートしていて、エディタ内でターミナルも開くことができる Visual Studio Code(VS Code)がお勧めです。
VS Code は TypeScript の開発元と同じ Microsoft によって開発されていて無料で利用できます。
関連ページ:VS Code で Web 制作
大まかな手順
以下は TypeScript を JavaScript にコンパイルするための環境を構築する大まかな手順です。
プロジェクトのディレクトリに TypeScript のパッケージをローカルインストールして、インストールされた TypeScript コンパイラ(tsc)を npx で実行してコンパイルします。
- プロジェクトのディレクトリを作成し、そのディレクトリに移動して、ターミナルで以下を実行
npm init -yでpackage.jsonを生成(必要に応じて編集)npm install -D typescriptで TypeScript コンパイラtscをローカルインストールnpm install -D @types/nodeで Node.js の型定義ファイルをローカルインストール(オプション:必要に応じて利用するライブラリとその型定義ファイルをインストール)npx tsc --initでtsconfig.jsonを生成(必要に応じて編集)npx tscを実行して TypeScript を JavaScript にコンパイル
TypeScript コンパイラのインストール
TypeScript を JavaScript にコンパイルするには、TypeScript コンパイラが必要になります。
任意の名前のプロジェクトのディレクトリを作成し、そこに TypeScript のパッケージ(コンパイラのファイルなど)をローカルインストールして環境を構築します。
ローカルインストールは特定のディレクトリにパッケージをインストールして、そのディレクトリだけで使う方法です。まずはディレクトリを作成し、インストールに必要な package.json を生成します。
この例ではプロジェクトのディレクトリの名前を tsp としています。
% mkdir tsp return //tsp という名前のディレクトリを作成 % cd tsp return //作成したディレクトリ tsp へ移動
package.json を生成
続いてプロジェクトのディレクトリで npm init コマンドに -y(または --yes)オプションを指定して実行し、package.json と言うファイルを生成します。
% npm init -y return //デフォルトの値を使って package.json を生成
// 生成される package.json のパスと設定が表示される
Wrote to /Applications/MAMP/htdocs/sample/tsp/package.json:
{
"name": "tsp",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC"
}
npm init に -y(または --yes)オプションを指定して実行すると、コマンドのレスポンスに表示されているデフォルトの値を使って package.json が生成されます。
package.json はプロジェクトにインストールされるパッケージの依存関係を管理するファイルで、プロジェクトの設定やタスクの登録なども記述することができます。この時点ではデフォルトのままで OK です。
typescript のインストール
package.json の準備ができたら、TypeScript のパッケージ(typescript)をインストールします。
このパッケージは開発時にのみ必要なパッケージなので npm install コマンドに --save-dev(または短縮形の -D)オプションを指定して実行します。
以下の場合、バージョンを指定していないのでパッケージの最新版がインストールされます。必要に応じてパッケージ名の後に @ を付けてバージョンを指定してインストールすることもできます。
% npm install --save-dev typescript return // パッケージの最新版をインストール added 1 package, and audited 2 packages in 900ms found 0 vulnerabilities
インストールを実行すると、node_modules というディレクトリが追加され、その中にインストールしたパッケージの中身が格納されます。また、package-lock.json というファイルも自動的に追加されます。
この時点でプロジェクトのディレクトリは以下のようになっています。
TypeScript コンパイラ(実行ファイル)は node_modules/typescript/bin/ に格納された tsc です。また、.bin ディレクトリが作成され、実行ファイルへのシンボリックリンクが格納されます。
tsp //プロジェクトのディレクトリ ├── node_modules │ ├── .bin //実行ファイルへのシンボリックリンクを格納するフォルダ │ │ ├── tsc //TypeScript コンパイラへのシンボリックリンク │ │ └── tsserver │ └── typescript //インストールしたパッケージの中身(モジュール) │ └── bin │ ├── tsc //TypeScript コンパイラ(実行ファイル) │ └── tsserver ├── package-lock.json └── package.json
この時点での package.json は以下のようになっています。
--save-dev オプションを指定して typescript パッケージをインストールしたので devDependencies フィールドに typescript がバージョン情報と共に追加されています(13行目)。
{
"name": "tsp",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"typescript": "^5.2.2"
}
}
コンパイル
ローカルインストールした TypeScript コンパイラの tsc コマンドを直接実行しようとすると「コマンドが見つかりません」というようなエラーになってしまいます。
以下は tsc コマンドに -v オプションを指定してバージョンを確認しようとしていますが、command not found というエラーになります。
% tsc -v return // バージョンを確認 zsh: command not found: tsc //エラー
npx コマンドを使用
ローカルインストールした TypeScript コンパイラ(tsc)を実行するには npx コマンドを使用します。
npx はローカルインストールしてプロジェクトの node_modules にインストールされたコマンド(実行ファイル)を実行するためのツールです。
% npx tsc -v return // バージョンを確認(npx コマンドを使用) Version 5.2.2 // バージョンが表示される
または、以下のように実行ファイルやシンボリックリンクへのパスを指定して実行することもできますが、上記のように npx を使った方が簡単です。
// パスを指定して実行 % ./node_modules/typescript/bin/tsc -v return // バージョンを確認 // 実行ファイルへのシンボリックリンクのパスを指定して実行 % ./node_modules/.bin/tsc -v return // バージョンを確認
tsc コマンドにファイルを指定する場合と指定しない場合
tsc コマンドを使ってコンパイルする際に、(コマンド引数として)コンパイル対象のファイルを指定する場合と指定しない場合では以下のように動作が異なります。
- ファイルを指定して実行:コンパイラのデフォルト及びコマンドラインオプションで指定された設定でコンパイルされ、
tsconfig.json(コンパイラの設定ファイル) は無視されます。 - ファイルを指定せずに実行:
tsconfig.jsonを検索して読み込み、その設定に従ってコンパイルされます。
ファイルを指定して tsc コマンドを実行
TypeScript の簡単なコードを書いてコンパイルしてみます。
この例では、以下のように src というディレクトリを作成して、その中に index.ts という TypeScript のファイルを配置します(ディレクトリやファイルの名前は任意の好きな名前を付けることができます)。
tsp //プロジェクトのディレクトリ
├── node_modules
│ └── typescript
├── package-lock.json
├── package.json
└── src //作成
└── index.ts //作成
src ディレクトリに配置した index.ts に以下の TypeScript のコードを記述します。
const message: string = "hello, world!"; console.log(message);
コンパイルするには、プロジェクトのディレクトリで npx で tsc コマンドにコンパイルするファイルを指定して実行します(ファイルを指定せずにコンパイルするには tsconfig.json を用意します)。
% npx tsc src/index.ts return //ファイルを指定してコンパイルを実行
指定するファイルは以下のようにグロブパターンで指定可能することもできます。
npx tsc src/*.ts return // src ディレクトリ内の全ての .ts ファイルをコンパイル
上記のようにファイルを指定して実行すると、コンパイラのデフォルトの設定でコンパイルされます。
上記の場合、出力先のオプションを何も指定していないので、同じディレクトリに同じファイル名でコンパイルした JavaScript ファイルが生成されます。
tsp
├── node_modules
│ └── typescript
├── package-lock.json
├── package.json
└── src
├── index.js // コンパイルされて生成されたファイル
└── index.ts
出力先を指定する場合は、--outDir オプションを指定します。以下の場合は dist ディレクトリに index.js が生成されます。
% npx tsc src/index.ts --outDir dist return //出力先を指定してコンパイルを実行
tsp
├── dist
│ └── index.js //コンパイルされて生成されたファイル
├── node_modules
│ └── typescript
├── package-lock.json
├── package.json
└── src
├── index.js // 不要なので削除
└── index.ts
以下が index.ts をコンパイルして生成された JavaScript のファイル index.js です。
TypeScript から JavaScript へのコンパイルでは、TypeScript に特有の部分が取り除かれ、プレインな JavaScript が生成されます。
var message = "hello, world!"; console.log(message);
node コマンドに上記の生成された JavaScript ファイルを指定して実行すると、ターミナルに「hello, world!」と出力されます。
% node dist/index.js return //node コマンドを実行 hello, world!
コマンドラインオプションの詳細は tsc CLI Options に掲載されています。
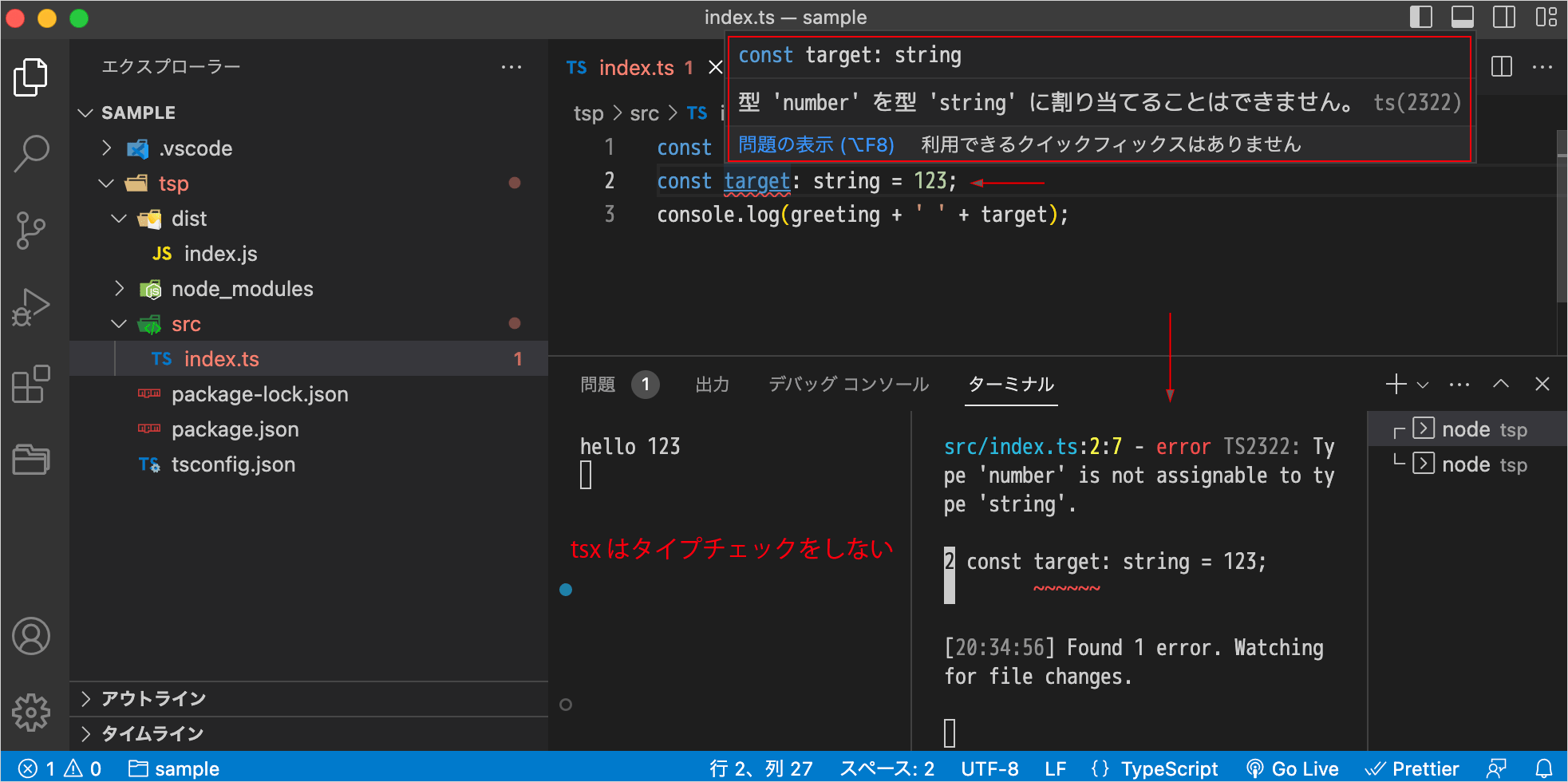
VS Code でのエラー
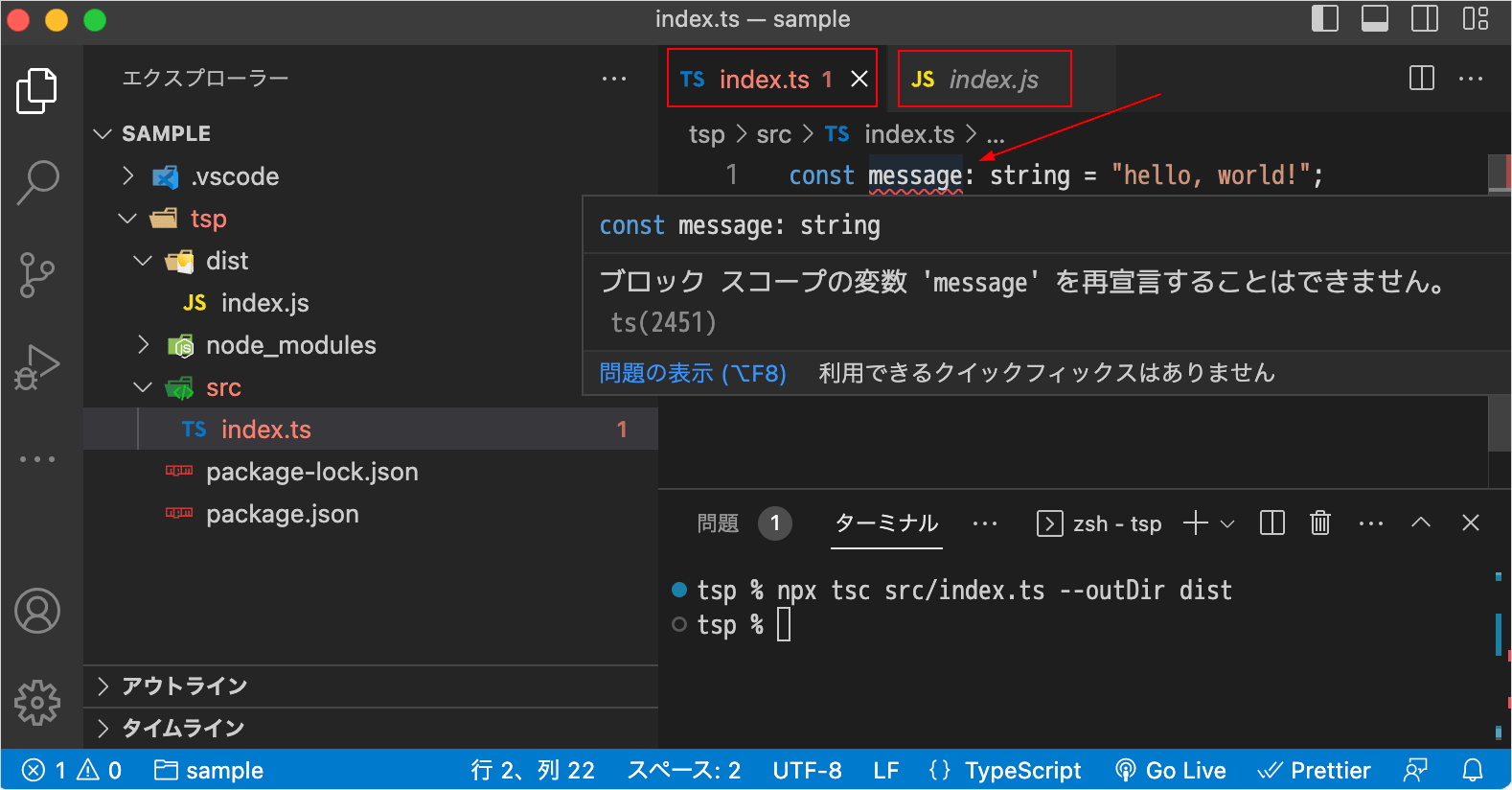
tsconfig.json を作成していない状態でコンパイルを実行して、VS Code で以下のように TypeScript のファイル(index.ts)とコンパイルされたファイル(index.js)を同時に開くとエラーにるかも知れません。
この例の場合、エラー部分にマウスを当てると「ブロックスコープの変数 'message' を再宣言することはできません ts(2451)」と表示されます。
ファイルを1つずつ開けば(同時に開かなければ)エラーにはなりません。
また、次項で作成する tsconfig.json を生成すればエラーは消えます(生成後読み込まれるまでにほんの少し時間がかかります)。
tsconfig.json を設定してコンパイル
前述のようにコマンドライン引数とオプションを指定してコンパイルすることもできますが、TypeScript コンパイラには様々なオプションがあるので、tsconfig.json を使ってコンパイラのオプションを設定してコンパイルする方法がよく使われます。
tsconfig.json は TypeScript のコンパイル設定(Compiler Options)を記述するファイルです。
以下のコマンドで tsconfig.json を生成することができます。
% npx tsc --init return //tsconfig.json を生成
デフォルトで生成される tsconfig.json にはたくさんのコメントアウトが付いていて、コメントアウトを外せばその設定を使えるようになっています。
以下は上記コマンドで生成された tsconfig.json のコメント部分を全て削除したものです。
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es2016",
"module": "commonjs",
"esModuleInterop": true,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,
"strict": true,
"skipLibCheck": true
}
}
この例では以下のように outDir オプションでコンパイルされた JavaScript ファイルの出力先(5行目)と include オプションでコンパイルの対象ファイル(11行目)を指定しています。
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es2016",
"module": "commonjs",
"outDir": "dist", // "outDir": "./dist" でも同じ
"esModuleInterop": true,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,
"strict": true,
"skipLibCheck": true
},
"include": ["./src/**/*.ts"] //追加(compilerOptions の外側に記述)
}
先の例で使用した index.ts をコンパイルしてみます。
ファイル構成は先の例でコンパイルされて出力された dist フォルダとその中の index.js は削除します(残しておいても上書きされるので問題ありません)。
tsp ├── node_modules │ └── typescript ├── package-lock.json ├── package.json ├── src │ └── index.ts └── tsconfig.json //コンパイラオプションの設定ファイル
tsconfig.json の設定内容に従ってコンパイルするので、以下のようにファイルを指定せずにコマンドを実行します。
% npx tsc return //コンパイルを実行
include オプションに ./src/**/*.ts を指定したので、src ディレクトリ内の全ての .ts ファイルがコンパイルされます。
そして outDir オプションに指定した dist ディレクトリが作成され、その中に同じファイル名のコンパイルされた JavaScript ファイルが生成されます。
tsp ├── dist │ └── index.js //コンパイルされて生成されたファイル ├── node_modules │ └── typescript ├── package-lock.json ├── package.json ├── src │ └── index.ts └── tsconfig.json //コンパイラオプションの設定ファイル
以下がコンパイルされて生成された index.js です。tsconfig.json の "strict": true により "use strict"; が出力され、"target": "es2016" により const が使われています(コマンドラインでファイルを指定してコンパイルした際は var となっていました)。
"use strict"; const message = "hello, world!"; console.log(message);
--showConfig 設定の表示
コマンドラインオプションに --showConfig を指定して実行すると、最終的なコンパイラオプションを表示することができます。
% npx tsc --showConfig return //コンパイラオプションを表示
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es2016",
"module": "commonjs",
"outDir": "./dist",
"esModuleInterop": true,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,
"strict": true,
"skipLibCheck": true
},
"files": [
"./src/index.ts"
],
"include": [
"./src/**/*.ts"
],
"exclude": [
"dist"
]
}
ファイル名を指定して実行すると、tsconfig.json の設定が無視されるのが確認できます。
//ファイル名を指定してコンパイルする場合のコンパイラオプション
% npx tsc --showConfig src/index.ts return
{
"compilerOptions": {},
"files": [
"./src/index.ts"
]
}
--watch オプション
tsc コマンドに --watch オプション(短縮形は -w )を指定して実行すると、.ts ファイルが更新されるたびに自動的に再コンパイルしてくれます(watch モード)。
% npx tsc --watch return // または npx tsc -w
上記を実行すると、以下のように watch モードになり、.ts ファイルの変更を監視します。
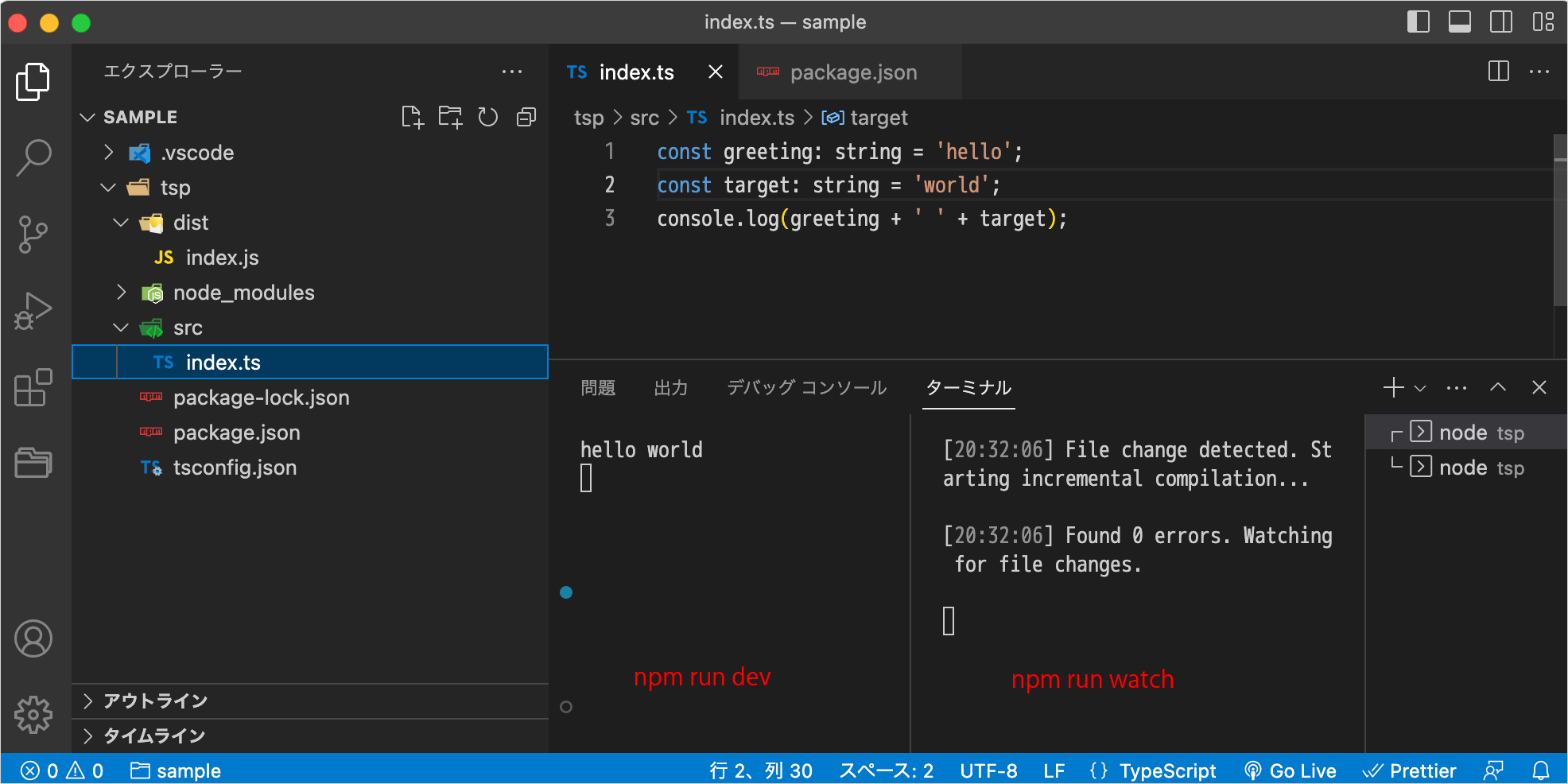
[10:39:03] Starting compilation in watch mode... //watch モードを開始 [10:39:03] Found 0 errors. Watching for file changes.
例えば、index.ts を変更して保存すると、自動的にコンパイルしてくれます。
[10:42:12] File change detected. Starting incremental compilation... //ファイル変更を検知して再コンパイル実行 [10:42:12] Found 0 errors. Watching for file changes.
watch モードの終了
watch モードを終了するには control + c を押します(プロンプトが戻ります)。
watch モードで別のコマンドを入力
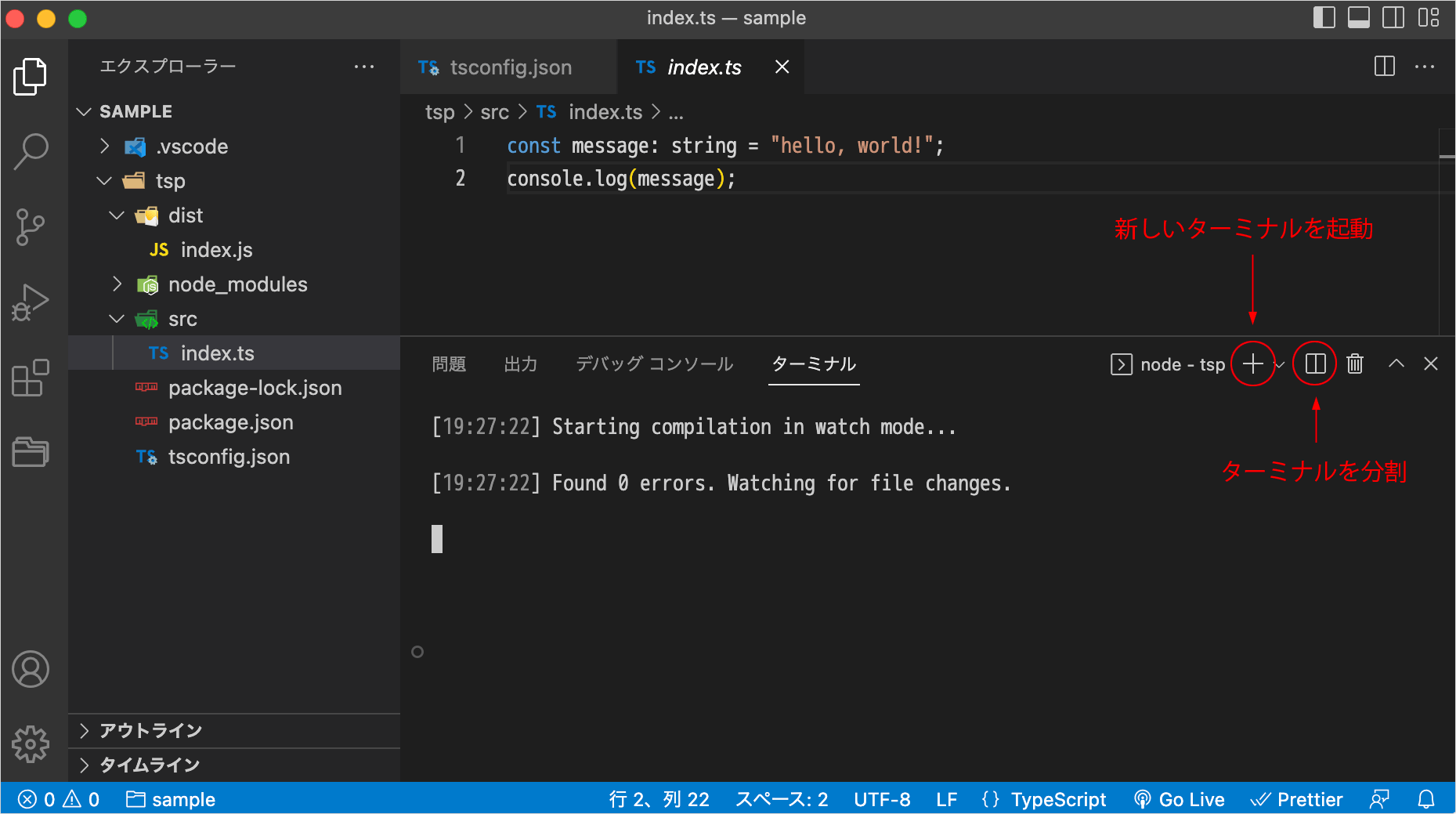
watch モードの状態で、別のコマンドを入力する場合は、新たに別のターミナルを開きます。
VS Code を使用している場合は、ターミナルのタブの + をクリックするか、control + shift + ` を押せば、新たなターミナルを起動することができます。
ターミナルの切り替えは右側に表示されている中から選択します。ターミナルを終了するには exit コマンドを実行します。
ターミナルを分割することもできます。ターミナルを分割するショートカットキーはエディタの分割と同じなので、ショートカットキーを使う場合はターミナルを選択した状態で command + \ を押します。
npm scripts
package.json の scripts フィールドにコマンドやスクリプトなどのタスクを指定すれば、npm run タスク名 で指定したタスクを実行することができます。
package.json に以下の7行目を設定すると、npm run watch で npx tsc --watch を実行することができます。ローカルインストールしたパッケージの実行ファイルを指定する場合は npx は不要です。
{
"name": "tsp",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"watch": "tsc --watch"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"typescript": "^4.9.5"
}
}
ターミナルで以下を実行すると watch モードになり、.ts ファイルが更新されると自動的にコンパイルされます。
% npm run watch retrun // npx tsc --watch が実行される //watch モードになり、ファイルが更新されると自動的にコンパイルされます [13:15:36] File change detected. Starting incremental compilation... [13:15:36] Found 0 errors. Watching for file changes. //終了するには control + c を押します ^C
npm start
以下のように特別なスクリプト名の start にタスクを指定すると、npm start だけでコマンドで実行することができます。
"scripts": {
"start": "tsc --watch"
},
% npm start retrun // npx tsc --watch が実行される
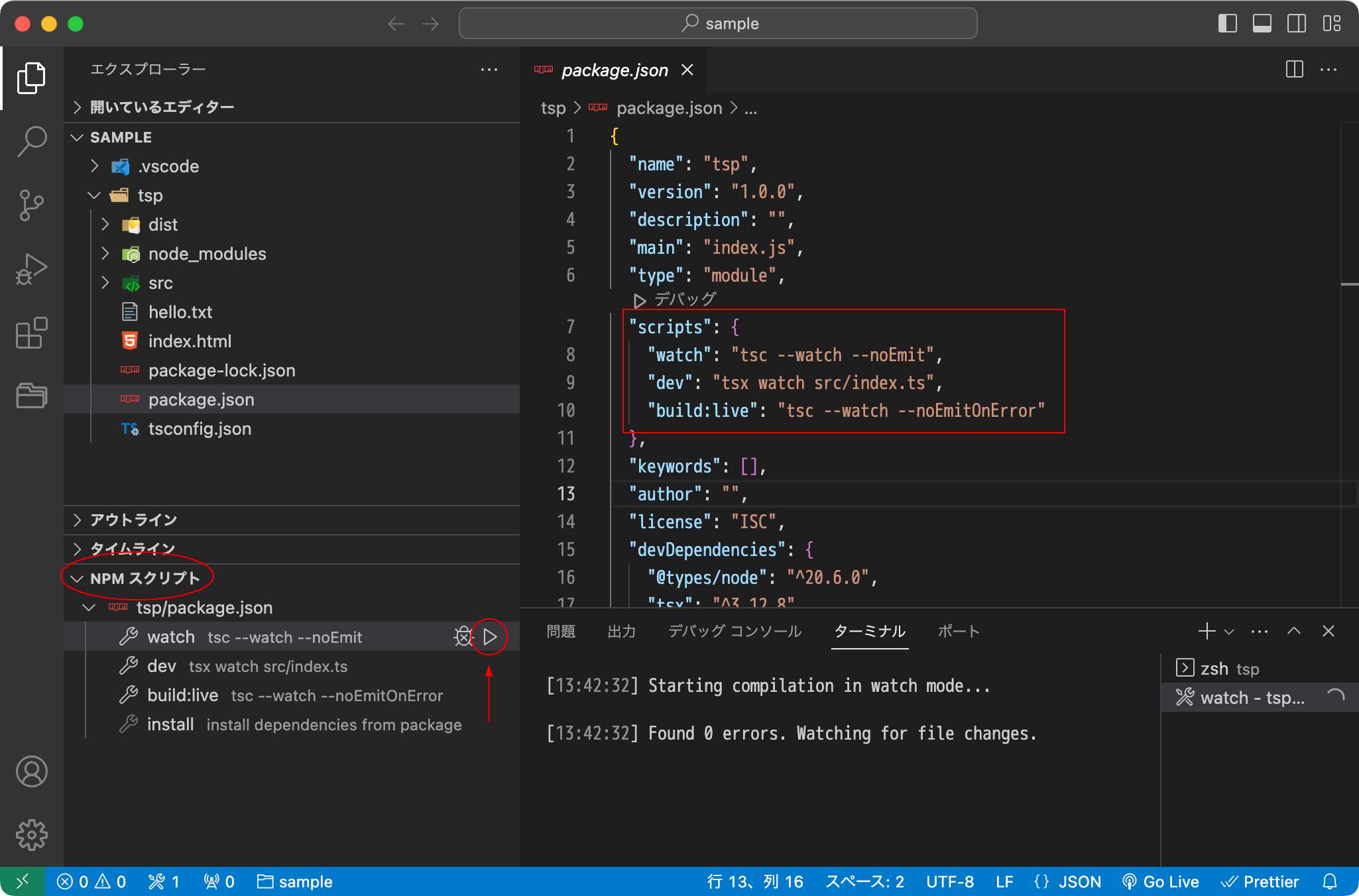
VS Code NPM スクリプトパネル
VS Code を使用していれば、左下に表示される NPM スクリプトパネルでクリックするだけで登録してある npm scripts を実行することができます。
プロジェクトを ES Modules に(Native ESM)
プロジェクト内の .js ファイルを ES Modules として扱うには以下を行います。
"type": "module" の指定により、.ts, .js ファイルの拡張子を変更せずに ES Modules として扱えるようになります。但し、CommonJS モジュールが扱えなくなります。
言い換えると、この設定により import を使用することを強制するので、require() を使用するとエラーになります。例えば、node コマンドで require() を使ったファイルを指定した場合、以下のようなエラーになります。
var fs = require('fs');
^
ReferenceError: require is not defined in ES module scope, you can use import instead
This file is being treated as an ES module because it has a '.js' file extension and '/Applications/MAMP/htdocs/sample/tsp/package.json' contains "type": "module". To treat it as a CommonJS script, rename it to use the '.cjs' file extension.
at file:///Applications/MAMP/htdocs/sample/tsp/dist/sample.js:2:10
at ModuleJob.run (node:internal/modules/esm/module_job:194:25)
package.json に "type": "module"
package.json に "type": "module" を追加します(以下では6行目に追加)。
{
"name": "tsp",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"type": "module",
"scripts": {
"watch": "tsc --watch"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"typescript": "^4.9.5"
}
}
tsconfig.json の "module" を変更
tsconfig.json の "module" を "esnext" または "nodenext" に変更します。使用するツールにより異なる可能性があります(デフォルトは commonjs)。
以下の例では、"target" を "es2020" に、"moduleResolution" を "node" に設定しています。
使用するツールによっては、以下の設定で機能しない場合もあるかも知れませんので、その場合は必要に応じて変更します(例: ts-node-dev を利用する場合は、module を nodenext とするなど)。
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es2020", // 変更(または esnext など)
"module": "esnext", // 変更(または nodenext)
"moduleResolution": "node", //または node16 や nodenext、または省略
"outDir": "./dist",
"esModuleInterop": true,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,
"strict": true,
"skipLibCheck": true
},
"include": ["./src/**/*.ts"]
}
ts-node を利用する場合
ts-node を利用する場合は、tsconfig.json に ts-node オプションとして "esm": true を追加します
スクリプトとモジュール
TypeScript と JavaScript のファイルはスクリプトとモジュールに分類することができます。
HTML の script 要素で JavaScript を読み込む際に、type="module" を指定した場合はモジュールとして扱われ、指定しない場合はスクリプトとして扱われます。type="module" を指定せずに読み込んだコードの中で import や export が使われていると構文エラーになります。
Node.js の場合は、package.json の "type": "module" が設定されていれば .js ファイルをモジュールとして扱います。この設定に関わらず、.cjs のファイルは常にスクリプト、.mjs のファイルは常にモジュールとして扱われます。
TypeScript の場合は、コード中に import や export が使われている場合は自動的にモジュールとして扱われ、そうでない場合はスクリプトとして扱われます(従来の判定方法。次項参照)。
TypeScript 4.7 での更新
TypeScript 4.7 で tsconfig.json の compilerOptions の module の設定項目に node16(nodenext)が追加されました。
{
"compilerOptions": {
"module": "esnext", // node16 と nodenext が設定可能になった
...
}
}
現時点では node16 と nodenext には違いがありませんが、将来的には nodenext は新しいバージョンの Node.js の仕様に追随することになります。
module を node16 に設定した場合は、ファイルがスクリプトかモジュールかの判定方法が従来の方法(コード中に import や export が使われているどうかでの判定)から変わります。
module に node16 や nodenext を設定した場合、.ts ファイルがスクリプトかモジュールかは package.json の type フィールドを参照して決められます。
module が node16 の場合、package.json が "type": "module" であれば、.ts ファイルを ES モジュールと解釈します(モジュールとして扱います)。
また、moduleDetection オプションでこの挙動を変更することができます(moduleDetection を force に設定すると、すべてのファイルがモジュールとして扱われます)。
moduleResolution を設定している場合は、module に設定した値に合わせて moduleResolution の設定も変更が必要になる場合があります。
詳細は以下のサイトのページに解説があります。
関連ページ:
参考:
ブラウザ(HTML)で表示
TypeScript のコードはブラウザで直接実行できないので、コンパイルした JavaScript ファイルを HTML ファイルで読み込みます。
この例では HTML ファイル(index.html)を作成してプロジェクトのルートに配置します(ファイル名や配置する位置は任意です)。
tss //プロジェクトのディレクトリ ├── dist │ └── index.js // HTML ファイルで読み込む JavaScript ├── index.html // HTML ファイルを追加 ├── node_modules │ └── typescript ├── package-lock.json ├── package.json ├── src │ └── index.ts └── tsconfig.json
HTML ファイルでは、script タグの src 属性にコンパイルされて生成される index.js を指定して読み込みます。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="ja"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>TypeScript Sample</title> </head> <body> <!-- 取得対象の要素 --> <div id="target"></div> </body> <!-- コンパイルされた JavaScript を読み込む --> <script src="dist/index.js"></script> </html>
index.ts に以下を記述して、HTML の id 属性が target の div 要素に変数 message の値(hello, world!)を出力します。
const message: string = "hello, world!";
console.log(message);
const target = document.getElementById('target') as HTMLInputElement;
target.textContent = message;
ターミナルで npx tsc を実行して index.ts をコンパイルします。
% npx tsc retrun // index.ts をコンパイル
問題なくコンパイルされれば、以下の index.js が dist ディレクトリにに生成されます。
"use strict";
const message = "hello, world!";
console.log(message);
const target = document.getElementById('target');
target.textContent = message;
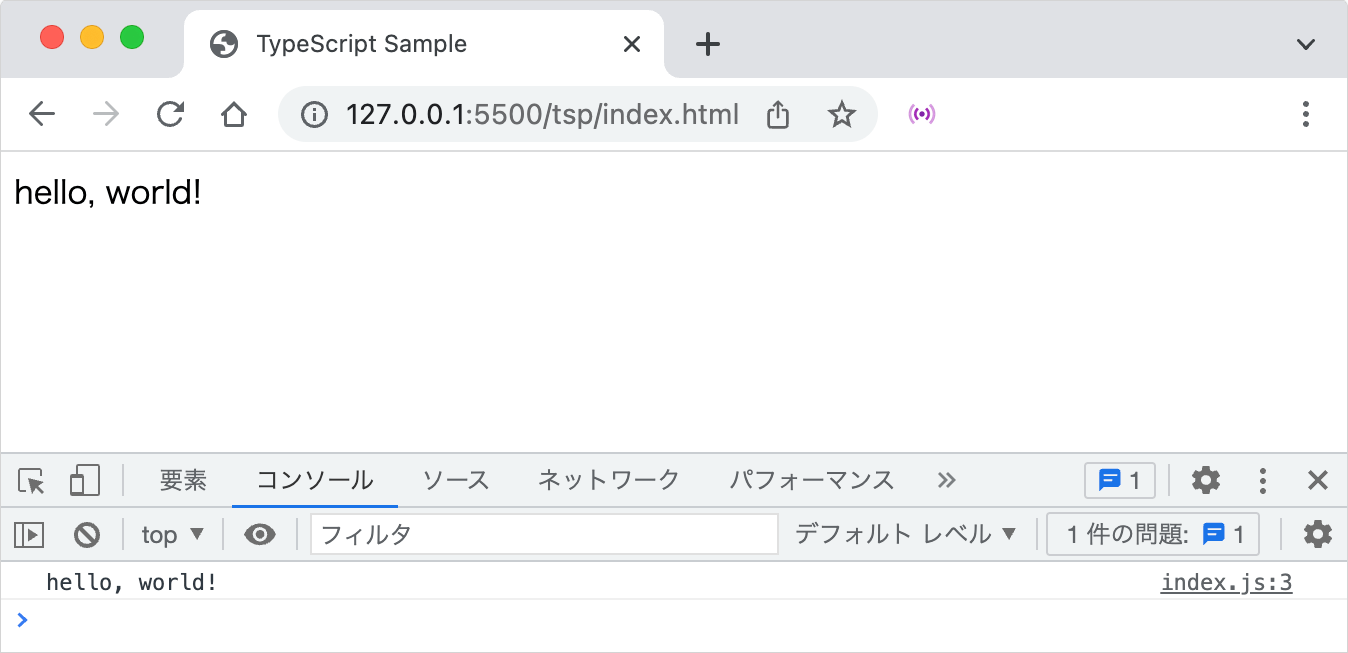
HTML ファイル(index.html)を任意のブラウザで開くと hello, world! と表示され、コンソールにも hello, world! と出力されます(以下はローカル環境で開いていますが、ファイルをダブルクリックすればデフォルトのブラウザで表示されます)。
--watch オプションを指定して tsc コマンドを実行すれば、.ts ファイルが更新されるたびに自動的に再コンパイルしてくれので便利です。
npx tsc --watch retrun // index.ts が更新されれば自動的にコンパイル
VS Code に 拡張機能の Live Server をインストールしてあれば、ブラウザも自動的に更新されます。
Node.js で実行
TypeScript のコードは Node.js で直接実行できないので、JavaScript にコンパイルしてから実行します。
また、Node の組み込みモジュールを使う場合は @types/node をインストールする必要があります。
例えば、以下のような組み込みモジュールの fs を使った TypeScript のコードを実行する場合、
import fs from 'fs'; //package.jsonに"type":"module"を設定しているので import を使う
fs.readFile('./hello.txt', 'utf8', function(err:unknown, data:string) {
if (err) {
console.log(err);
}
else {
console.log(data);
}
})
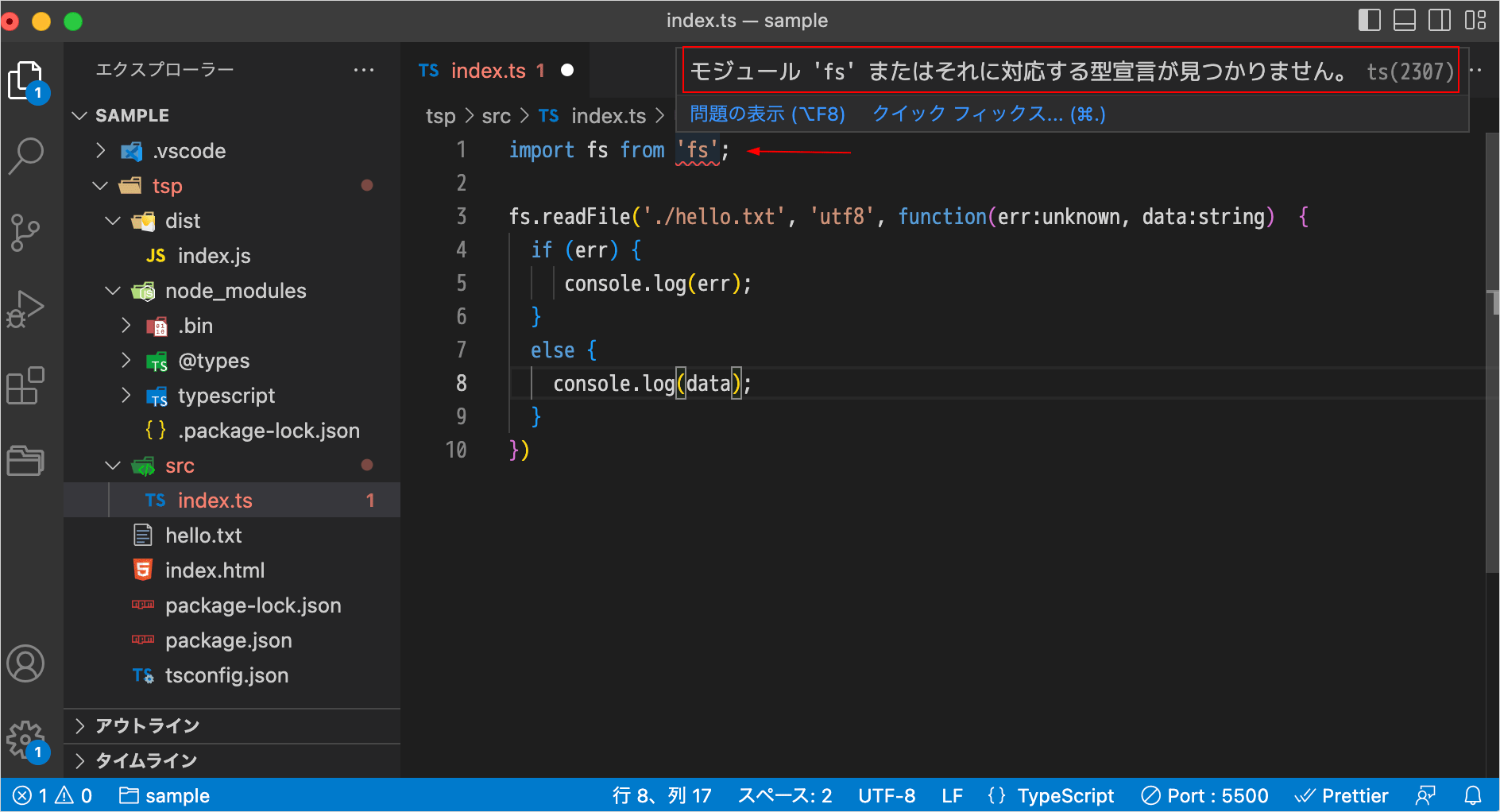
npx tsc を実行してコンパイルしようとすると、以下のように「fs モジュールまたはそれに対応する型宣言が見つかりません」というエラーになります。
% npx tsc return // コンパイルを実行
src/index.ts:1:16 - error TS2307: Cannot find module 'fs' or its corresponding type declarations.
1 import fs from 'fs';
~~~~
Found 1 error in src/index.ts:1
VS Code を使っている場合は、上記のコードを記述した時点で(コンパイルを実行する前に)エディタにエラーが出ます。
@types/ から始まるパッケージ
@types/ から始まる名前のパッケージは JavaScript のライブラリに型定義を付与するための型定義ファイルが入ったパッケージです。TypeScript 向けの型定義が同梱されていない JavaScript のライブラリ(パッケージ)を使用する場合に利用します。
言い換えると、使用したい JavaScript ライブラリに型定義がない(型定義が同梱されていない)場合は、それに対応した @types パッケージをインストールして型定義を補うことで、そのライブラリを TypeScript で利用できるようになります。
@types/ から始まる名前のパッケージは型定義を補うためのパッケージなので、その中には JavaScript のライブラリ本体は入っていません。
使い方は、@types/ から始まる名前のパッケージ(例:node の場合は @types/node)をインストールするだけで、ライブラリを型定義付きで(つまり、TypeScript で)使えるようになります。
型定義ファイルの拡張子は .d.ts になります。
前述の例の場合、Node.js のライブラリ本体には型定義が存在しないのでエラーになっているため、@types/node という Node.js の型定義ファイルが入ったパッケージをインストールする必要があります。
例えば、型定義が同梱されていない Express を利用する場合は、express と @types/express をインストールします。
@types パッケージは有志によって作られていて、@types パッケージの開発・運用は DefinitelyTyped コミュニティにより行われています。現在広く使われている JavaScript のパッケージについては、ほとんどが対応する @types パッケージが存在しますが、マイナーなパッケージについては @types パッケージが作成されていない場合もあります。
@types/node をインストール
Node の組み込みモジュールを使ったコードがコンパイルできるようにするため @types/node をインストールします。
% npm install --save-dev @types/node return //@types/node をインストール added 1 package, and audited 3 packages in 513ms found 0 vulnerabilities
@types/node が node_modules の中に追加されます。前述の fs を使ったコードのファイル index.ts をコンパイルして確認するため、hello.txt という「Hello from hello.txt!」という文字列を記述したテキストファイルを追加します。
tss //プロジェクトのディレクトリ ├── dist │ └── index.js ├── hello.txt //テキストファイルを追加 ├── node_modules │ ├── @types │ │ └── node │ └── typescript ├── package-lock.json ├── package.json ├── src │ └── index.ts // コンパイルするファイル └── tsconfig.json
Hello from hello.txt!
再度、先程の index.ts を npx tsc コマンドを実行してでコンパイルすると今度は問題なくコンパイルされ、以下の index.js が dist ディレクトリに出力されます。
※require()ではなくimportを使っているのは package.json に"type":"module"を設定して、プロジェクト内の .js ファイルを ES Modules として扱うようにしているためです。
import fs from 'fs';
fs.readFile('./hello.txt', 'utf8', function (err, data) {
if (err) {
console.log(err);
}
else {
console.log(data);
}
});
node コマンドにコンパイルされた JavaScript ファイル(index.js)を指定して実行すると、hello.txt に記述されているテキストがターミナルに出力されます。
% node dist/index.js return Hello from hello.txt! //hello.txt に記述されているテキスト
以下はこの時点での package.json と tsconfig.json です。
{
"name": "tsp",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"type": "module",
"scripts": {
"watch": "tsc --watch"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"@types/node": "^20.6.0",
"typescript": "^5.2.2"
}
}
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es2020",
"module": "esnext",
"moduleResolution": "node",
"outDir": "./dist",
"esModuleInterop": true,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,
"strict": true,
"skipLibCheck": true
},
"include": ["./src/**/*.ts"]
}
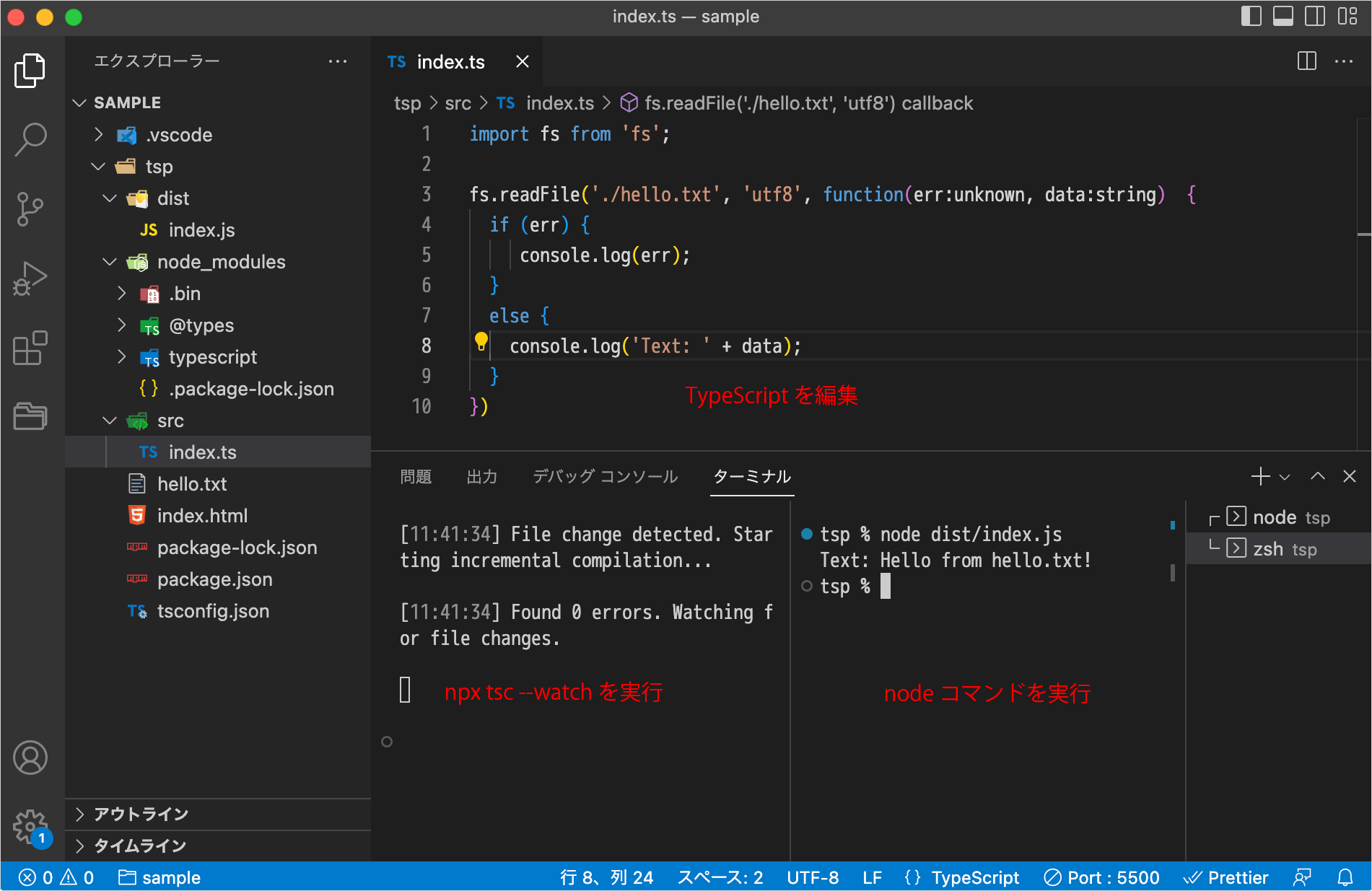
VS Code を使用している場合は、TypeScript ファイルを編集しながら、ターミナルを分割して1つのターミナルでは npx tsc --watch を実行してファイルの更新を監視(更新されたら自動的にコンパイル)して、別のターミナルで node コマンドを実行することができます。
TypeScript を直接 Node.js で実行
Node.js は TypeScript を直接実行することはできないため、TypeScript をまず JavaScript にコンパイルしてから Node.js で実行するという2ステップになり、少し面倒です。
以下のいずれかのツールを利用すると TypeScript を直接 Node.js で実行することができます。※ これらのツールはコンパイルは行わないので、コンパイルは別途実行します。
以下以外にも様々なツールがあります。
| ツール | 概要(説明) |
|---|---|
| tsx | 内部ではトランスパイルに esbuild が使われていて、ts-node より速く TypeScript ファイルを実行できます。また、watch モードもあります。package.json に "type": "module" を指定しても特別な設定をする必要がありません。但し、型チェック(type checking)は行わないので別途対応が必要です。 |
| esbuild-register | tsx 同様、内部ではトランスパイルに esbuild が使われていて、ts-node より速く TypeScript ファイルを実行できます。また、watch モードを指定することもできます(experimental feature)。package.json に "type": "module" を指定している場合は --loader フラグを指定する必要があります(experimental feature)。tsx 同様、型チェック(type checking)は行わないので別途対応が必要です。 |
| ts-node | TypeScript を直接 Node.js で実行することができます。package.json に "type": "module" を指定している場合は、追加で tsconfig.json にオプションを指定する必要があります。watch モードはないので、必要であれば nodemon などを利用します。 |
| nodemon | nodemon を利用すれば、TypeScript ファイルを更新すると自動的に ts-node を呼び出して node コマンドを実行することができます。ts-node がインストールされている必要があります。 |
| ts-node-dev | nodemon 同様、TypeScript ファイルを更新すると自動的に ts-node を呼び出して node を実行することができます。nodemon より高速ですが、package.json に "type": "module" を指定しているとエラーになります。 |
個人的には tsx が設定も簡単で処理も高速なので気に入っています。
tsx
tsx(TypeScript Execute)は CommonJS と ES Modules の両方で、TypeScript をシームレスに実行するための CLI コマンドです。node コマンドの代わりに tsx コマンドに TypeScript ファイルを直接指定して実行できます。
tsx は TypeScript と ESM ファイルを実行するために ESBuild で拡張された Node.js で、内部では ESBuild を使用しているので高速です。
TypeScript Execute (tsx): Node.js enhanced with esbuild to run TypeScript & ESM files
Blazing fast on-demand TypeScript & ESM compilation
2023/9 の時点では Node.js v12~18 ではテスト済みで、Node.js v20 はまだサポートされておらず、いろいろとバグがあるようです(tsx issues)。
tsx を利用するには tsx のパッケージをインストールします。
% npm install --save-dev tsx return // tsx をインストール
以下はこの時点での package.json と tsconfig.json です。
{
"name": "tsp",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"type": "module",
"scripts": {
"watch": "tsc --watch"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"@types/node": "^20.6.0",
"tsx": "^3.12.8",
"typescript": "^5.2.2"
}
}
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es2020",
"module": "esnext",
"moduleResolution": "node",
"outDir": "./dist",
"esModuleInterop": true,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,
"strict": true,
"skipLibCheck": true
},
"include": ["./src/**/*.ts"]
}
tsx を実行
tsx は node の代替として設計されているため、Node.js と同じように使用できます。 すべてのコマンドライン引数 (一部を除く) が Node.js に伝達されます(tsx はコンパイルは行いません)。
npx で tsx コマンドに直接 TypeScript ファイルを指定して実行します。
% npx tsx src/index.ts return // TypeScript ファイルを指定して実行 Hello from hello.txt!
カスタム tsconfig.json
デフォルトでは、tsconfig.json は現在の作業ディレクトリから検出されますが、--tsconfig フラグでカスタム tsconfig.json を指定することもできます。
//カスタム設定ファイル(./path/to/tsconfig.custom.json)を指定して実行 % npx tsx --tsconfig ./path/to/tsconfig.custom.json src/index.ts return
watch モード
watch オプションを指定すると、ファイルの変更を検知して自動的に実行することができます。
% npx tsx watch src/index.ts return
watch モードを終了するには control + c を押します。
スクリーンをクリアしない
デフォルトでは、変更を検知して自動的に実行する際に、スクリーンがクリアされて結果が表示されますが、--clear-screen=false を指定するとスクリーンをクリアしません。
% npx tsx watch --clear-screen=false src/index.ts
型チェック(type checking)
tsx は型チェック(型検査)をしません。
そのため、型チェックは IDE 側(例 VS Code)で行うか、tsc --noEmit コマンドを別途実行します。tsc --noEmit とすることで TypeScript のコンパイルエラーのみをチェックできます。
--noEmit はコンパイルしたファイルを生成しないようにする(型チェックだけ実行して JavaScript ファイルの出力は行わない)コマンドラインオプションです。
例えば、package.json の scripts フィールド に以下を設定して
"scripts": {
"watch": "tsc --watch --noEmit",
"dev": "tsx watch src/index.ts"
},
1つのターミナルで npm run dev を実行し、別のターミナルで npm run watch を実行すれば tsx を watch モードで実行し、タイプチェックをすることもできます。
以下は VS Code でターミナルを分割して npm run dev と npm run watch を実行する例です。
tsx はタイプチェックをせずに実行されますが、エディタ(VS Code)の IntelliSense と tsc --noEmit でタイプチェックが行われます。
コンパイルも実行
例えば、package.json の scripts フィールド に以下を設定して
"scripts": {
"watch": "tsc --watch --noEmit",
"dev": "tsx watch src/index.ts",
"build:live": "tsc --watch --noEmitOnError"
},
1つのターミナルで npm run dev を実行し、別のターミナルで npm run build:live を実行すれば tsx を watch モードで実行し、コンパイルが成功した時のみファイルを生成することもできます。
--noEmitOnError はコンパイルが成功した時のみファイルを生成するコマンドラインオプションです。
コマンドラインオプションの代わりに、tsconfig.json に "noEmit": true や "noEmitOnError": true を指定することもできます。
tsx の削除
インストールした tsx を削除(アンインストール)するには、インストールしたディレクトリで npm uninstall コマンドを実行します。
npm uninstall tsx return // tsx をアンインストール
esbuild-register
esbuild-register は tsx 同様、内部ではトランスパイルに esbuild が使われていて、ts-node より速く TypeScript ファイルを Node.js で実行できます。
esbuild-registerを利用するにはesbuildとesbuild-registerのパッケージをインストールします。
//esbuild と esbuild-register をインストール % npm install --save-dev esbuild esbuild-register return
以下がこの時点での package.json です。devDependenciesにesbuildとesbuild-registerが追加されています。また、scriptsフィールドのdevに watch モード(後述)でのコマンドを登録しています。
{
"name": "tsp",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"type": "module",
"scripts": {
"watch": "tsc --watch",
"dev": "node --loader esbuild-register/loader -r esbuild-register --watch src/index.ts"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"@types/node": "^20.6.0",
"esbuild": "^0.19.2",
"esbuild-register": "^3.4.2",
"typescript": "^5.2.2"
}
}
使い方は他のツールとは異なり、node コマンドに -r(または --require)オプションで esbuild-register を指定して、TypeScript ファイルを指定して実行します。
但し、この例の場合、package.json に "type": "module" を指定しているので以下を実行するとエラーになります。
% node -r esbuild-register src/index.ts return
package.json に "type": "module" を指定している場合
package.json に "type": "module" を指定している場合、TypeScript ファイルをロードするには、 以下のように --loader フラグを指定する必要があります(長いので package.json の scripts フィールドに登録すると良いと思います)。
% node --loader esbuild-register/loader -r esbuild-register src/index.ts return // Custom ESM Loaders が Experimental である(変更になる可能性がある)との警告が表示されます (node:29935) ExperimentalWarning: Custom ESM Loaders is an experimental feature and might change at any time (Use `node --trace-warnings ...` to show where the warning was created) Hello from hello.txt! //実行結果
watch モード
node コマンドの --watch を指定できます。
% node --loader esbuild-register/loader -r esbuild-register --watch src/index.ts // Custom ESM Loaders と Watch mode が Experimental であるとの警告が表示されます (node:30262) ExperimentalWarning: Watch mode is an experimental feature and might change at any time (Use `node --trace-warnings ...` to show where the warning was created) (node:30263) ExperimentalWarning: Custom ESM Loaders is an experimental feature and might change at any time (Use `node --trace-warnings ...` to show where the warning was created) Hello from hello.txt! //実行結果 Completed running 'src/index.ts' //監視中 // 変更を実施 Restarting 'src/index.ts' (node:30629) ExperimentalWarning: Custom ESM Loaders is an experimental feature and might change at any time (Use `node --trace-warnings ...` to show where the warning was created) data: Hello from hello.txt! //実行結果 Completed running 'src/index.ts' //監視中 ^C // control + c で watch モードを終了
型チェック
esbuild-register は tsx 同様、型チェックをしないので、型チェックは IDE 側(例 VS Code)で行うか、tsc --noEmit コマンドを別途実行します。
esbuild-register の削除
削除するにはインストールしたディレクトリで以下を実行します。
% npm uninstall esbuild esbuild-register //esbuild と esbuild-register を削除
ts-node
ts-node を利用すると TypeScript を直接 Node.js で実行することができ、型チェックもしてくれます。
但し、tsx 同様、ts-node は TypeScript を直接 Node.js で実行するためのツールでコンパイルはしません。コンパイルは、別途 tsc コマンドで行う必要があります。
ts-node を利用するには ts-node のパッケージをインストールします。
% npm install --save-dev ts-node return //ts-node をインストール % npx ts-node -v return //ts-node のバージョンを確認 v10.9.1
以下がこの時点での package.json です。devDependencies に ts-node が追加されています。
{
"name": "tsp",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"type": "module",
"scripts": {
"watch": "tsc --watch"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"@types/node": "^20.6.0",
"ts-node": "^10.9.1",
"typescript": "^5.2.2"
}
}
ts-node をインストールしたら、npxでts-nodeコマンドに対象の.tsファイルを指定して実行ます。
.tsフ ァイルから Node.js を直接実行できるはずですが、この例の場合、package.json で "type": "module" を指定しているので、以下のようなエラーになります。
% npx ts-node src/index.ts
TypeError [ERR_UNKNOWN_FILE_EXTENSION]: Unknown file extension ".ts" for /Applications/MAMP/htdocs/sample/tss/src/index.ts
at new NodeError (node:internal/errors:400:5)
at Object.getFileProtocolModuleFormat [as file:] (node:internal/modules/esm/get_format:79:11)
at defaultGetFormat (node:internal/modules/esm/get_format:121:38)
at defaultLoad (node:internal/modules/esm/load:81:20)
at nextLoad (node:internal/modules/esm/loader:163:28)
at ESMLoader.load (node:internal/modules/esm/loader:605:26)
at ESMLoader.moduleProvider (node:internal/modules/esm/loader:457:22)
at new ModuleJob (node:internal/modules/esm/module_job:64:26)
at ESMLoader.#createModuleJob (node:internal/modules/esm/loader:480:17)
at ESMLoader.getModuleJob (node:internal/modules/esm/loader:434:34) {
code: 'ERR_UNKNOWN_FILE_EXTENSION'
}
package.json の "type": "module" を削除すればエラーは出なくなりますが、"type": "module" を削除したくない場合は、以下のように --esm オプションを指定します。
% npx ts-node --esm src/index.ts return //ts-node コマンドに --esm オプションを指定
tsconfig.json に ts-node オプションを追加
または、tsconfig.json に ts-node のオプションとして "esm": true を追加します。
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es2020",
"module": "esnext",
"moduleResolution": "node",
"outDir": "./dist",
"esModuleInterop": true,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,
"strict": true,
"skipLibCheck": true,
},
"include": ["./src/**/*.ts"],
// 以下のオプションを追加
"ts-node": {
"esm": true
}
}
上記のように tsconfig.json に ts-node のオプションを追加すれば、実行時に --esm オプションを指定する必要はありません。
% npx ts-node src/index.ts return
型チェックを外すオプション
ts-node は tsx に比べるとトランスパイルが遅いですが、型チェックをしないようにすることで多少速くなるようです。型チェックを外すには --transpileOnly(または -T) オプションを指定します。
% npx ts-node --transpileOnly src/index.ts
watch モードはない
ts-node には変更を監視してリロードする機能(watch モード)はありません。
ファイルの変更時に ts-node プロセスを再起動する場合は、nodemon、ts-node-dev などのツールを利用します(Watching and restarting)。
ts-node の削除
ts-node を削除するには以下を実行します。事項の nodemon や ts-node-dev を利用するには ts-node がインストールされている必要があります。
% npm uninstall ts-node return
参考:
nodemon
nodemon は Node.js の CLI で、ファイルが更新されたときに自動的に実行プロセスを再起動することで開発を効率化してくれるツールです。
nodemon を利用すれば、TypeScript ファイルを更新すると自動的に ts-node を呼び出して node コマンドを実行することができます(ts-node がインストールされている必要があります)。
nodemon を利用するには nodemon のパッケージをインストールします。
% npm install --save-dev nodemon return //nodemon をインストール
以下がこの時点での package.json です。devDependencies に nodemon が追加されています。
{
"name": "tsp",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"type": "module",
"scripts": {
"watch": "tsc --watch"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"@types/node": "^20.6.0",
"nodemon": "^3.0.1",
"ts-node": "^10.9.1",
"typescript": "^5.2.2"
}
}
以下はこの時点での tsconfig.json です。ts-node インストール時と同じです。
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es2020",
"module": "esnext",
"moduleResolution": "node",
"outDir": "./dist",
"esModuleInterop": true,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,
"strict": true,
"skipLibCheck": true
},
"include": ["./src/**/*.ts"],
// package.json に "type": "module" を指定する場合は以下を設定
"ts-node": {
"esm": true
}
}
一番簡単な使い方は、npx で nodemon コマンドに対象の .ts ファイルを指定して実行するだけです。
% npx nodemon src/index.ts return [nodemon] 3.0.1 [nodemon] to restart at any time, enter `rs` [nodemon] watching path(s): *.* [nodemon] watching extensions: ts,json [nodemon] starting `ts-node src/index.ts` //自動的に ts-node src/index.ts が実行される Hello from hello.txt! // ts-node src/index.ts の実行結果 [nodemon] clean exit - waiting for changes before restart //変更を監視
src/index.ts を変更して保存すると、自動的に ts-node src/index.ts が実行されます。終了するには control + c を押します。
[nodemon] restarting due to changes... // 変更を検知して実行プロセスを再起動 [nodemon] starting `ts-node src/index.ts` //自動的に ts-node src/index.ts を実行 Data: Hello from hello.txt! //実行結果 [nodemon] clean exit - waiting for changes before restart //変更を監視 ^C //終了するには control + c を押します
ファイルを指定しないで実行すると、package.json の "main" フィールドで指定されているファイルを読み込もうとします。この例の場合、 "main" はデフォルトの index.js のままなので以下のようにエラーになります。control + c で終了します。
% npx nodemon return //ファイルを指定しないで実行
[nodemon] 3.0.1
[nodemon] to restart at any time, enter `rs`
[nodemon] watching path(s): *.*
[nodemon] watching extensions: js,mjs,json
[nodemon] starting `node index.js`
node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1042
throw err;
^
//package.json の "main" で指定されているファイルを探すがないのでエラー
Error: Cannot find module '/Applications/MAMP/htdocs/sample/tss/index.js'
at Module._resolveFilename (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1039:15)
at Module._load (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:885:27)
at Function.executeUserEntryPoint [as runMain] (node:internal/modules/run_main:81:12)
at node:internal/main/run_main_module:23:47 {
code: 'MODULE_NOT_FOUND',
requireStack: []
}
Node.js v18.13.0
[nodemon] app crashed - waiting for file changes before starting...
package.json の "main" に対象のファイル "src/index.ts" を指定しておけば、ファイルを指定しないで実行することもできます。
コンパイルも実行する
前述の例の場合、TypeScript ファイルを JavaScript ファイルにコンパイルせずに node を実行しているため、JavaScript ファイルへのコンパイルは行われません(ts-node は TypeScript を直接実行するためのツールでコンパイルはしません)。
JavaScript ファイルへのコンパイル(ビルド)も同時に行いたい場合は以下のように --exec オプションを指定して tsc コマンドも実行するようにします。
% npx nodemon --exec 'tsc && ts-node' src/index.ts
コマンドラインオプション
コマンドラインに指定できるオプションは npx nodemon -h で確認できます。
% npx nodemon -h return
Usage: nodemon [options] [script.js] [args]
Options:
--config file ............ alternate nodemon.json config file to use
-e, --ext ................ extensions to look for, ie. js,pug,hbs.
-x, --exec app ........... execute script with "app", ie. -x "python -v".
-w, --watch path ......... watch directory "path" or files. use once for
each directory or file to watch.
-i, --ignore ............. ignore specific files or directories.
-V, --verbose ............ show detail on what is causing restarts.
-- <your args> ........... to tell nodemon stop slurping arguments.
Note: if the script is omitted, nodemon will try to read "main" from
package.json and without a nodemon.json, nodemon will monitor .js, .mjs, .coffee,
.litcoffee, and .json by default.
For advanced nodemon configuration use nodemon.json: nodemon --help config
See also the sample: https://github.com/remy/nodemon/wiki/Sample-nodemon.json
Examples:
$ nodemon server.js
$ nodemon -w ../foo server.js apparg1 apparg2
$ nodemon --exec python app.py
$ nodemon --exec "make build" -e "styl hbs"
$ nodemon app.js -- --config # pass config to app.js
All options are documented under: nodemon --help options
nodemon.json
設定ファイル nodemon.json を作成してプロジェクトのルートに配置し、nodemon の動作をカスタマイズすることもできます。
以下は verbose プロパティに true を指定して詳細情報を表示するようにし、execMap プロパティで .ts ファイルの場合は tsc コマンドと ts-node コマンドを実行(JavaScript ファイルにコンパイルして ts-node を実行)するように指定する例です。
{
"verbose": true,
"execMap": {
"ts": "tsc && ts-node"
}
}
以下は上記を設定した場合の実行例です。"verbose": true を指定しているので詳細な情報が表示され、tsc(コンパイル)と ts-node が実行されています。
% npx nodemon src/index.ts return [nodemon] 3.0.1 [nodemon] reading config ./nodemon.json [nodemon] to restart at any time, enter `rs` [nodemon] or send SIGHUP to 35300 to restart [nodemon] watching path(s): *.* [nodemon] watching extensions: ts,json [nodemon] starting `tsc && ts-node src/index.ts` [nodemon] spawning [nodemon] child pid: 35316 [nodemon] watching 8 files [nodemon] files triggering change check: dist/index.js [nodemon] matched rule: **/*.* [nodemon] changes after filters (before/after): 1/0 Hello from hello.txt! //起動時の実行結果 [nodemon] clean exit - waiting for changes before restart [nodemon] files triggering change check: src/index.ts [nodemon] matched rule: **/*.* [nodemon] changes after filters (before/after): 1/1 [nodemon] restarting due to changes... [nodemon] src/index.ts [nodemon] starting `tsc && ts-node src/index.ts` [nodemon] spawning [nodemon] child pid: 35357 [nodemon] files triggering change check: dist/index.js [nodemon] matched rule: **/*.* [nodemon] changes after filters (before/after): 1/0 Data: Hello from hello.txt! //変更時の実行結果 [nodemon] clean exit - waiting for changes before restart
npx nodemon --help options や npx nodemon --help config で設定のオプションなどを確認することができます。
設定ファイルサンプルページ:sample-nodemon.md
npm scripts
package.json の scripts フィールドに npm scripts(タスク)を登録する例です。
以下の例では前述の設定ファイル nodemon.json は使わないので、削除するか、または空 {} にします。
{
"name": "tsp",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"type": "module",
"scripts": {
"start": "nodemon src/index.ts",
"watch": "tsc --watch",
"build": "tsc",
"build:live": "nodemon --exec 'tsc && ts-node' src/index.ts"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"@types/node": "^20.6.0",
"nodemon": "^3.0.1",
"ts-node": "^10.9.1",
"typescript": "^5.2.2"
}
}
上記を設定すると、以下のようなコマンドが実行できます。
npm start または npm run start を実行すると、nodemon src/index.ts が実行され、index.ts が変更されると、ts-node により node が実行されます。
% npm start return > tsp@1.0.0 start > nodemon src/index.ts [nodemon] 3.0.1 [nodemon] to restart at any time, enter `rs` [nodemon] watching path(s): *.* [nodemon] watching extensions: ts,json [nodemon] starting `ts-node src/index.ts` Data: Hello from hello.txt! [nodemon] clean exit - waiting for changes before restart
npm run watch を実行すると tsc --watch が実行され、index.ts が変更されるたびに、tsc が実行されコンパイルされます。
npm run build を実行すると tsc が実行されコンパイルされます。
npm run build:live を実行すると、nodemon --exec 'tsc && ts-node' src/index.ts が実行され、index.ts が変更されるたびに、tsc が実行されてコンパイルされ、ts-node により node が実行されます。
nodemon の削除
nodemon を削除するには以下を実行します。
% npm uninstall nodemon return
ts-node-dev
ts-node-dev を利用すると、tsx や nodemon 同様、TypeScript ファイルを更新すると自動的に ts-node を呼び出して node を実行することができます
ts-node-dev は TypeScript 実行エンジンおよびコンパイルプロセスと直接やり取りするので nodemon などよりも処理が速いです。
但し、ts-node-dev は ts-node のネイティブの ESM(ES Module)ローダーと互換性がないので、この例のように package.json で "type": "module" を指定している場合などではエラーになります。
以下は ts-node のページ(Watching and restarting)からの抜粋です。
Note that ts-node-dev is incompatible with our native ESM loader.
関連ページ:ES Module error: Cannot use import statement outside a module #265
※ ネイティブの ES Module を扱う(package.json の "type": "module" を削除したくない)場合は前述の tsx や nodemon を利用することができます。
ts-node-dev を利用するには ts-node-dev のパッケージをインストールします。
% npm install --save-dev ts-node-dev return //ts-node-dev をインストール
使い方は、--respawn オプションと監視対象の .ts ファイルを指定して実行します。但し、package.json で "type": "module" を指定していると以下のようにエラーになります。
% npx ts-node-dev --respawn src/index.ts return
[INFO] 13:57:28 ts-node-dev ver. 2.0.0 (using ts-node ver. 10.9.1, typescript ver. 5.2.2)
Compilation error in /Applications/MAMP/htdocs/sample/tsp/src/index.ts
Error: Must use import to load ES Module: /Applications/MAMP/htdocs/sample/tsp/src/index.ts
at Object.<anonymous> (/Applications/MAMP/htdocs/sample/tsp/src/index.ts:1:7)
at Module._compile (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1218:14)
at Module._compile (/Applications/MAMP/htdocs/sample/tsp/node_modules/source-map-support/source-map-support.js:568:25)
at Module.m._compile (/private/var/folders/kv/pf49drlx3617xb8zdz07hkph0000gn/T/ts-node-dev-hook-730330802323822.js:69:33)
at Module._extensions..js (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1272:10)
at require.extensions..jsx.require.extensions..js (/private/var/folders/kv/pf49drlx3617xb8zdz07hkph0000gn/T/ts-node-dev-hook-730330802323822.js:114:20)
at require.extensions.<computed> (/private/var/folders/kv/pf49drlx3617xb8zdz07hkph0000gn/T/ts-node-dev-hook-730330802323822.js:71:20)
at Object.nodeDevHook [as .ts] (/Applications/MAMP/htdocs/sample/tsp/node_modules/ts-node-dev/lib/hook.js:63:13)
at Module.load (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1081:32)
at Function.Module._load (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:922:12)
[ERROR] 13:57:28 Error: Must use import to load ES Module: /Applications/MAMP/htdocs/sample/tsp/src/index.ts
^C //control + c で終了
関連ページ:[ERROR] Must use import to load ES module #314
また、この例の場合、tsconfig.json の module オプションが esnext では以下のようなエラーになったので、"module": "nodenext" とする必要がありました。
% npx ts-node-dev --respawn src/index.ts
[INFO] 14:01:07 ts-node-dev ver. 2.0.0 (using ts-node ver. 10.9.1, typescript ver. 5.2.2)
(node:35882) Warning: To load an ES module, set "type": "module" in the package.json or use the .mjs extension.
(Use `node --trace-warnings ...` to show where the warning was created)
/Applications/MAMP/htdocs/sample/tsp/src/index.ts:1
import fs from 'fs';
^^^^^^
SyntaxError: Cannot use import statement outside a module
at internalCompileFunction (node:internal/vm:74:18)
at wrapSafe (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1141:20)
at Module._compile (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1182:27)
at Module._compile (/Applications/MAMP/htdocs/sample/tsp/node_modules/source-map-support/source-map-support.js:568:25)
at Module.m._compile (/private/var/folders/kv/pf49drlx3617xb8zdz07hkph0000gn/T/ts-node-dev-hook-037162082741870384.js:69:33)
at Module._extensions..js (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1272:10)
at require.extensions..jsx.require.extensions..js (/private/var/folders/kv/pf49drlx3617xb8zdz07hkph0000gn/T/ts-node-dev-hook-037162082741870384.js:114:20)
at require.extensions.<computed> (/private/var/folders/kv/pf49drlx3617xb8zdz07hkph0000gn/T/ts-node-dev-hook-037162082741870384.js:71:20)
at Object.nodeDevHook [as .ts] (/Applications/MAMP/htdocs/sample/tsp/node_modules/ts-node-dev/lib/hook.js:63:13)
at Module.load (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1081:32)
[ERROR] 14:01:08 SyntaxError: Cannot use import statement outside a module
^C //control + c で終了
以下が、エラーなく動作した際の package.json と tsconfig.json です。
"type": "module" を削除)
{
"name": "tsp",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"watch": "tsc --watch"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"@types/node": "^20.6.0",
"ts-node": "^10.9.1",
"ts-node-dev": "^2.0.0",
"typescript": "^5.2.2"
}
}
"module" を "nodenext" に変更、"moduleResolution": "node" を削除)
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es2020",
"module": "nodenext",
"outDir": "dist",
"esModuleInterop": true,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,
"strict": true,
"skipLibCheck": true
},
"include": ["./src/**/*.ts"],
}
上記変更で動作しました。
% npx ts-node-dev --respawn src/index.ts return [INFO] 14:11:16 ts-node-dev ver. 2.0.0 (using ts-node ver. 10.9.1, typescript ver. 5.2.2) Hello from hello.txt! //実行結果 [INFO] 14:11:32 Restarting: /Applications/MAMP/htdocs/sample/tsp/src/index.ts has been modified Data: Hello from hello.txt! //.ts ファイルを更新すると自動的にコンパイルされ、実行される ^C //終了するには control + c を押します
ts-node-dev の削除
ts-node-dev を削除するには以下を実行します。
% npm uninstall ts-node-dev return
tsconfig.json
tsconfig.json は TypeScript のコンパイル設定を記述するファイルです(tsconfig.json を設定してコンパイル)。
tsconfig.json を生成するには npx tsc --init を実行します。
% npx tsc --init return //tsconfig.json を生成 Created a new tsconfig.json with: //以下のコンパイラオプションが設定された tsconfig.json が生成されます target: es2016 module: commonjs strict: true esModuleInterop: true skipLibCheck: true forceConsistentCasingInFileNames: true You can learn more at https://aka.ms/tsconfig
本来 JSON にはコメント機能はありませんが、TypeScript ではコメント付きの JSON が解釈できるようになっています。
デフォルトで生成される tsconfig.json にはたくさんのコメントアウトが付いて、コメントアウトを外せばその設定を使えるようになっています。
以下は生成された tsconfig.json のコメント部分を削除したもので、npx tsc --init を実行した際のレスポンスに表示されたコンパイラオプションが有効になっています(必要に応じて変更します)。
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es2016",
"module": "commonjs",
"esModuleInterop": true,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,
"strict": true,
"skipLibCheck": true
}
}
{
"compilerOptions": {
/* Visit https://aka.ms/tsconfig to read more about this file */
/* Projects */
// "incremental": true, /* Save .tsbuildinfo files to allow for incremental compilation of projects. */
// "composite": true, /* Enable constraints that allow a TypeScript project to be used with project references. */
// "tsBuildInfoFile": "./.tsbuildinfo", /* Specify the path to .tsbuildinfo incremental compilation file. */
// "disableSourceOfProjectReferenceRedirect": true, /* Disable preferring source files instead of declaration files when referencing composite projects. */
// "disableSolutionSearching": true, /* Opt a project out of multi-project reference checking when editing. */
// "disableReferencedProjectLoad": true, /* Reduce the number of projects loaded automatically by TypeScript. */
/* Language and Environment */
"target": "es2016", /* Set the JavaScript language version for emitted JavaScript and include compatible library declarations. */
// "lib": [], /* Specify a set of bundled library declaration files that describe the target runtime environment. */
// "jsx": "preserve", /* Specify what JSX code is generated. */
// "experimentalDecorators": true, /* Enable experimental support for TC39 stage 2 draft decorators. */
// "emitDecoratorMetadata": true, /* Emit design-type metadata for decorated declarations in source files. */
// "jsxFactory": "", /* Specify the JSX factory function used when targeting React JSX emit, e.g. 'React.createElement' or 'h'. */
// "jsxFragmentFactory": "", /* Specify the JSX Fragment reference used for fragments when targeting React JSX emit e.g. 'React.Fragment' or 'Fragment'. */
// "jsxImportSource": "", /* Specify module specifier used to import the JSX factory functions when using 'jsx: react-jsx*'. */
// "reactNamespace": "", /* Specify the object invoked for 'createElement'. This only applies when targeting 'react' JSX emit. */
// "noLib": true, /* Disable including any library files, including the default lib.d.ts. */
// "useDefineForClassFields": true, /* Emit ECMAScript-standard-compliant class fields. */
// "moduleDetection": "auto", /* Control what method is used to detect module-format JS files. */
/* Modules */
"module": "commonjs", /* Specify what module code is generated. */
// "rootDir": "./", /* Specify the root folder within your source files. */
// "moduleResolution": "node", /* Specify how TypeScript looks up a file from a given module specifier. */
// "baseUrl": "./", /* Specify the base directory to resolve non-relative module names. */
// "paths": {}, /* Specify a set of entries that re-map imports to additional lookup locations. */
// "rootDirs": [], /* Allow multiple folders to be treated as one when resolving modules. */
// "typeRoots": [], /* Specify multiple folders that act like './node_modules/@types'. */
// "types": [], /* Specify type package names to be included without being referenced in a source file. */
// "allowUmdGlobalAccess": true, /* Allow accessing UMD globals from modules. */
// "moduleSuffixes": [], /* List of file name suffixes to search when resolving a module. */
// "resolveJsonModule": true, /* Enable importing .json files. */
// "noResolve": true, /* Disallow 'import's, 'require's or '<reference>'s from expanding the number of files TypeScript should add to a project. */
/* JavaScript Support */
// "allowJs": true, /* Allow JavaScript files to be a part of your program. Use the 'checkJS' option to get errors from these files. */
// "checkJs": true, /* Enable error reporting in type-checked JavaScript files. */
// "maxNodeModuleJsDepth": 1, /* Specify the maximum folder depth used for checking JavaScript files from 'node_modules'. Only applicable with 'allowJs'. */
/* Emit */
// "declaration": true, /* Generate .d.ts files from TypeScript and JavaScript files in your project. */
// "declarationMap": true, /* Create sourcemaps for d.ts files. */
// "emitDeclarationOnly": true, /* Only output d.ts files and not JavaScript files. */
// "sourceMap": true, /* Create source map files for emitted JavaScript files. */
// "outFile": "./", /* Specify a file that bundles all outputs into one JavaScript file. If 'declaration' is true, also designates a file that bundles all .d.ts output. */
// "outDir": "./", /* Specify an output folder for all emitted files. */
// "removeComments": true, /* Disable emitting comments. */
// "noEmit": true, /* Disable emitting files from a compilation. */
// "importHelpers": true, /* Allow importing helper functions from tslib once per project, instead of including them per-file. */
// "importsNotUsedAsValues": "remove", /* Specify emit/checking behavior for imports that are only used for types. */
// "downlevelIteration": true, /* Emit more compliant, but verbose and less performant JavaScript for iteration. */
// "sourceRoot": "", /* Specify the root path for debuggers to find the reference source code. */
// "mapRoot": "", /* Specify the location where debugger should locate map files instead of generated locations. */
// "inlineSourceMap": true, /* Include sourcemap files inside the emitted JavaScript. */
// "inlineSources": true, /* Include source code in the sourcemaps inside the emitted JavaScript. */
// "emitBOM": true, /* Emit a UTF-8 Byte Order Mark (BOM) in the beginning of output files. */
// "newLine": "crlf", /* Set the newline character for emitting files. */
// "stripInternal": true, /* Disable emitting declarations that have '@internal' in their JSDoc comments. */
// "noEmitHelpers": true, /* Disable generating custom helper functions like '__extends' in compiled output. */
// "noEmitOnError": true, /* Disable emitting files if any type checking errors are reported. */
// "preserveConstEnums": true, /* Disable erasing 'const enum' declarations in generated code. */
// "declarationDir": "./", /* Specify the output directory for generated declaration files. */
// "preserveValueImports": true, /* Preserve unused imported values in the JavaScript output that would otherwise be removed. */
/* Interop Constraints */
// "isolatedModules": true, /* Ensure that each file can be safely transpiled without relying on other imports. */
// "allowSyntheticDefaultImports": true, /* Allow 'import x from y' when a module doesn't have a default export. */
"esModuleInterop": true, /* Emit additional JavaScript to ease support for importing CommonJS modules. This enables 'allowSyntheticDefaultImports' for type compatibility. */
// "preserveSymlinks": true, /* Disable resolving symlinks to their realpath. This correlates to the same flag in node. */
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true, /* Ensure that casing is correct in imports. */
/* Type Checking */
"strict": true, /* Enable all strict type-checking options. */
// "noImplicitAny": true, /* Enable error reporting for expressions and declarations with an implied 'any' type. */
// "strictNullChecks": true, /* When type checking, take into account 'null' and 'undefined'. */
// "strictFunctionTypes": true, /* When assigning functions, check to ensure parameters and the return values are subtype-compatible. */
// "strictBindCallApply": true, /* Check that the arguments for 'bind', 'call', and 'apply' methods match the original function. */
// "strictPropertyInitialization": true, /* Check for class properties that are declared but not set in the constructor. */
// "noImplicitThis": true, /* Enable error reporting when 'this' is given the type 'any'. */
// "useUnknownInCatchVariables": true, /* Default catch clause variables as 'unknown' instead of 'any'. */
// "alwaysStrict": true, /* Ensure 'use strict' is always emitted. */
// "noUnusedLocals": true, /* Enable error reporting when local variables aren't read. */
// "noUnusedParameters": true, /* Raise an error when a function parameter isn't read. */
// "exactOptionalPropertyTypes": true, /* Interpret optional property types as written, rather than adding 'undefined'. */
// "noImplicitReturns": true, /* Enable error reporting for codepaths that do not explicitly return in a function. */
// "noFallthroughCasesInSwitch": true, /* Enable error reporting for fallthrough cases in switch statements. */
// "noUncheckedIndexedAccess": true, /* Add 'undefined' to a type when accessed using an index. */
// "noImplicitOverride": true, /* Ensure overriding members in derived classes are marked with an override modifier. */
// "noPropertyAccessFromIndexSignature": true, /* Enforces using indexed accessors for keys declared using an indexed type. */
// "allowUnusedLabels": true, /* Disable error reporting for unused labels. */
// "allowUnreachableCode": true, /* Disable error reporting for unreachable code. */
/* Completeness */
// "skipDefaultLibCheck": true, /* Skip type checking .d.ts files that are included with TypeScript. */
"skipLibCheck": true /* Skip type checking all .d.ts files. */
}
}
以下はこのページの例で設定しているオプションの簡単な説明です。
| オプション | 説明 |
|---|---|
| target | どの JS 機能が古い JavaScript 構文にトランスパイルされ、どの機能がそのまま残されるかを設定します。 例えば target が ES5 以下である場合、アロー関数は function 式へ変換されます。以下を指定可能。
|
| module | モジュールに関する構文をどのように扱うかのオプション。以下のいずれかを指定可能。
|
| moduleResolution | モジュール解決の方法。npm でインストールしたモジュールを TypeScript が認識できるようにするオプション。デフォルトの classic は TypeScript のバージョン 1.6 のリリース前に使用されていたもので、最新のコードで classic を使用する必要はありません。以下のいずれかを指定可能。
|
| outDir | コンパイルされた .js ファイルの出力先の指定。指定しない場合は、.js ファイルは .ts ファイルを作成した(同じ)ディレクトリに出力されます。 |
| esModuleInterop | true にすると、すべてのインポートに対して CommonJS と ES Modules 間で相互運用可能なコードを出力します。 |
| forceConsistentCasingInFileNames | true にすると、インクルードするファイル名の大文字小文字を区別します(ケースがあっていない場合はエラーにします)。 |
| strict | strict 系のコンパイラオプションを一括で有効化するオプションです。true にすると、推奨される項目がまとめて有効化されます(strict 系のオプション 参照)。 |
| skipLibCheck | 型定義ファイルのチェックをスキップしてコンパイル実行時間を削減します。 |
| include | プログラムに含めるファイル名またはパターンのリストを配列で指定します。 ファイル名は tsconfig.json ファイルが配置されているディレクトリからの相対パスとして解決されます。 |
| noEmit | true にすると、JavaScript ソースコード、ソースマップ、型定義のファイルを出力しない(型チェックだけ実行して JavaScript ファイルの出力は行わない)ようにします(デフォルトは false)。これにより、Babel や swc などの TypeScript ファイルを JavaScript 環境内で実行可能なファイルへ変換するための別のツールを追加できます。 TypeScript をエディター統合やソースコードの型チェックツールとして利用できるようになります。 |
| noEmitOnError | true にすると、エラーがあるときに、JavaScript ソースコードやソースマップファイル、型定義ファイルなどをコンパイラに出力させない(コンパイルが成功した時のみファイルを生成する)ようにします。デフォルト値は false です。 |
| lib | TypeScript には組み込みの JS API やブラウザーで利用される API の型定義がデフォルトで組み込まれています。また、指定した target に合致する新しい JS 機能の API の型定義も TypeScript には組み込まれています。このオプションで標準の型定義として何を使うかを個別に指定することができます。 |
| listFiles | コンパイルされるファイル名を出力します。TypeScript がコンパイルしてほしいファイルを対象に含めてくれているかが分からないときなどに確認するために利用できます。 |
| explainFiles | TypeScript がプロジェクトの一部として認識するファイルの名前と、それらがコンパイルの一部である理由を出力します。このオプションはそれらのファイルがコンパイルの一部になった理由をデバッグすることを目的としています。 |
include と exclude
include と exclude を使ってコンパイル対象とするファイルやフォルダを指定することができます。
include で対象とするディレクトリやファイルを指定し、exclude で除外するディレクトリやファイルを指定して、この組み合わせで処理対象を限定します。
include と exclude には配列を指定します。また、以下のグロブパターン(簡単なワイルドカード)が使えます。
*ゼロ個以上の文字列にマッチ(ディレクトリセパレータは除く)?任意の 1 文字にマッチ(ディレクトリセパレータは除く)**/任意階層の任意ディレクトリにマッチ
以下の場合、src ディレクトリと foo ディレクトリの配下の全ての .ts ファイルをコンパイル対象としますが、src/bar/ の中のファイルは除く(対象外)という意味になります。
{
"compilerOptions": {
...
},
"include": ["src/**/*.ts", "foo/**/*.ts"],
"exclude": ["src/bar/*.ts"]
}
グロブパターンがファイルの拡張子を含まない場合、サポートされる拡張子のみが含まれるようになります(例:.ts、.tsx と .d.ts はデフォルトでインクルードされ、.js と .jsx は allowJs が設定された場合のみインクルードされます)。
include と exclude のどちらも指定しない場合、TypeScript コンパイラはプロジェクトのディレクトリやその配下のディレクトリを調べ、すべての .ts ファイルや .tsx ファイルをコンパイルしようとします(node_modules なども含まれてしまいます)。
また、TypeScript コンパイラがコンパイルの対象とするのは、include で指定されたファイルやディレクトリだけではなく、それらのファイルから import されたファイルも含みます。言い換えると、include はコンパイルの起点となるファイルやディレクトリを指定するオプションと言えます。
exclude について
exclude は、include で指定されたファイルやディレクトリから、その一部を除外したい場合に使用するためのオプションで、include とセットで使わないと意味がありません。
exclude で指定されたファイルはコンパイルの起点にはなりませんが、別のファイルから import された場合はコンパイルの対象となります。このため、exclude で指定してもそのファイルがコンパイルされてしまう場合は、別のファイルから import されている可能性があります。
files
コンパイルの対象を指定するオプションとして files もありますが、グロブパターンが使えず、コンパイル対象にするファイル名を配列で指定する必要があります。
{
"compilerOptions": { ... },
"files": [
"core.ts",
"sys.ts",
"types.ts",
"scanner.ts",
"parser.ts",
"utilities.ts",
"binder.ts",
"checker.ts",
"tsc.ts"
]
}
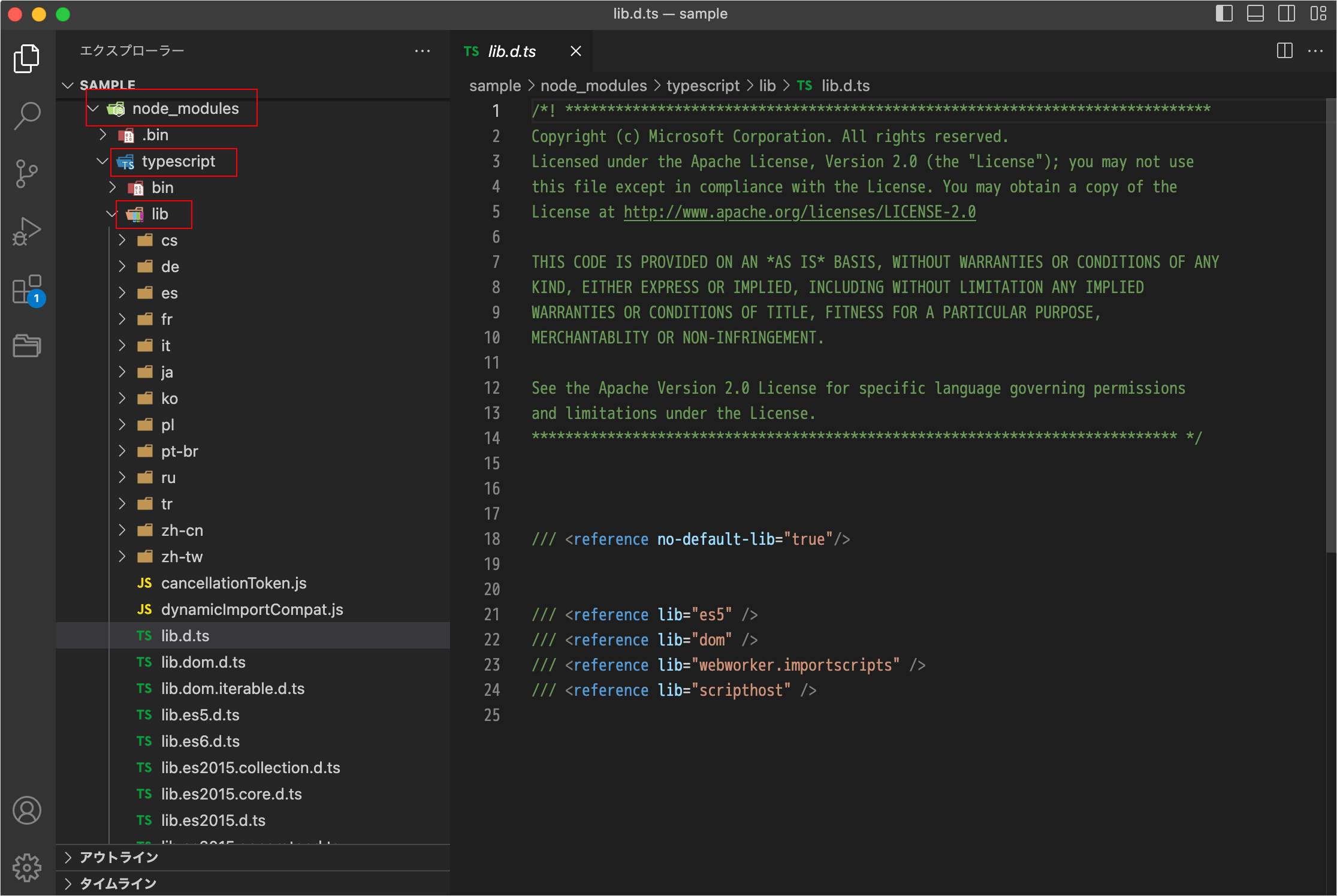
lib.d.ts
lib.d.ts は TypeScript をインストールした時に付属している型定義ファイルで、JavaScript API や DOM API の型定義ファイルなどが含まれています。
このファイルの目的は TypeScript のプロジェクトですぐに型のサポートを得られるようにすることで、TypeScript をインストールしたらすぐに様々な型定義が使えるのはこのためです。
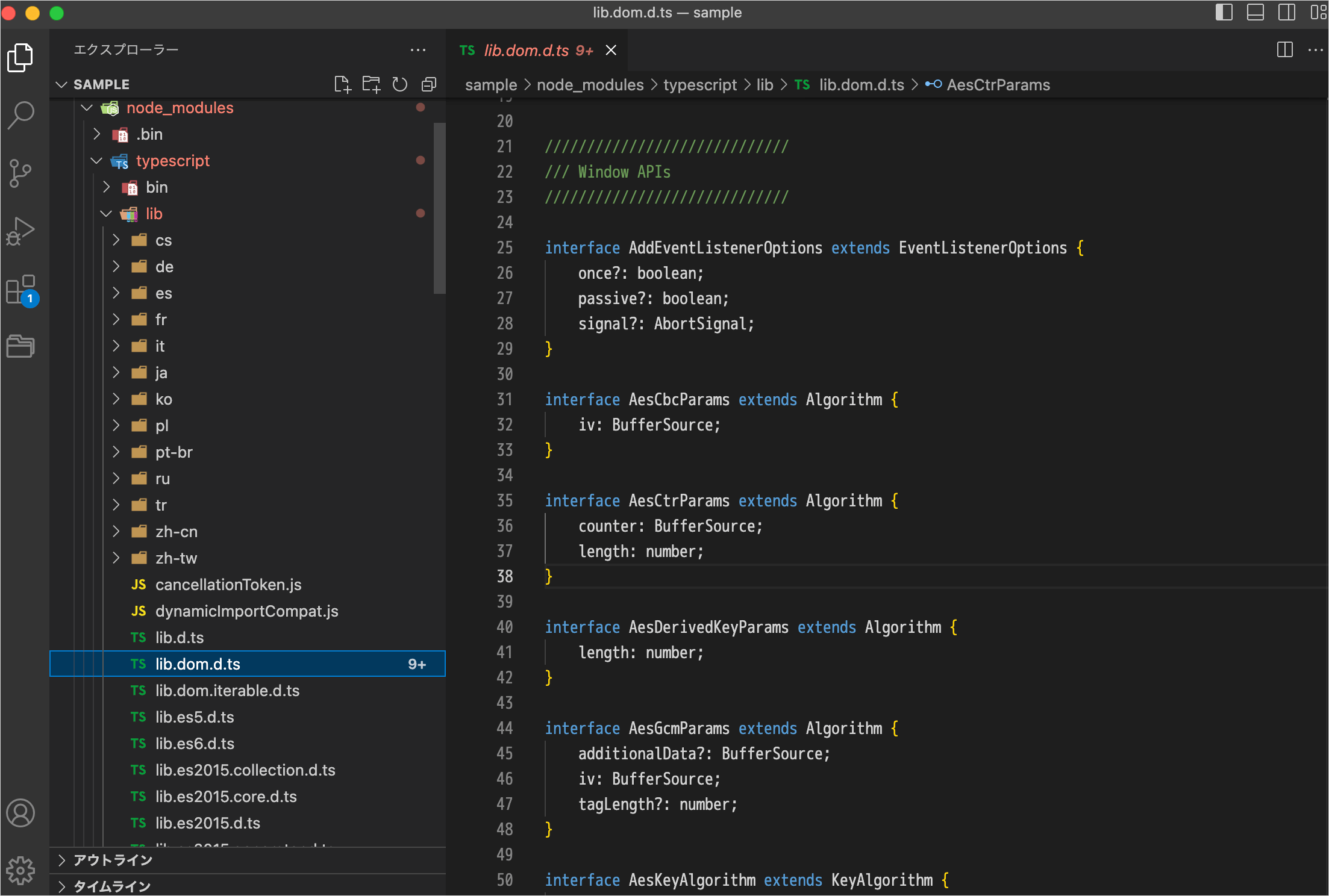
lib.dom.d.ts
TypeScript は JavaScript の型指定されたスーパーセットであり、DOM API の型定義(lib.dom.d.ts)が付属していて、デフォルトの TypeScript プロジェクトですぐに利用できるようになっています。
言い換えると、TypeScript はグローバル実行環境に DOM 型付けを使用します。
TypeScript ドキュメント:DOM Manipulation
lib.dom.d.ts を見てみると、DOM 関連のアンビエント宣言(declare キーワードを使った変数の型情報の宣言)が多数あるのが確認できます。
もし、DOM の定義ファイルなど特定の定義ファイルが不要な場合は、lib オプションで標準の型定義として何を使うかを個別に指定できます。
listFiles オプション
tsconfig.json の compilerOptions で "listFiles": true を指定してコンパイルを実行するか、コマンドラインオプションに --listFiles を指定してコンパイルを実行すると、TypeScript がコンパイルの対象としているファイルを確認することができます。
例えば、以下のような tsconfig.json の設定で、
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es5",
"module": "commonjs",
"outDir": "dist",
"esModuleInterop": true,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,
"strict": true,
"skipLibCheck": true
},
"include": ["./src/**/*.ts"]
}
--listFiles オプションを指定してコンパイルを実行すると以下のように出力されます。
% npx tsc --listFiles /Applications/.../node_modules/typescript/lib/lib.d.ts /Applications/.../node_modules/typescript/lib/lib.es5.d.ts /Applications/.../node_modules/typescript/lib/lib.dom.d.ts /Applications/.../node_modules/typescript/lib/lib.webworker.importscripts.d.ts /Applications/.../node_modules/typescript/lib/lib.scripthost.d.ts /Applications/.../src/index.ts
--explainFiles を指定すれば、それらがコンパイルの一部である理由も出力してくれます。
% npx tsc --explainFiles node_modules/typescript/lib/lib.d.ts Default library for target 'es5' node_modules/typescript/lib/lib.es5.d.ts Library referenced via 'es5' from file 'node_modules/typescript/lib/lib.d.ts' node_modules/typescript/lib/lib.dom.d.ts Library referenced via 'dom' from file 'node_modules/typescript/lib/lib.d.ts' node_modules/typescript/lib/lib.webworker.importscripts.d.ts Library referenced via 'webworker.importscripts' from file 'node_modules/typescript/lib/lib.d.ts' node_modules/typescript/lib/lib.scripthost.d.ts Library referenced via 'scripthost' from file 'node_modules/typescript/lib/lib.d.ts' src/index.ts Matched by include pattern './src/**/*.ts' in 'tsconfig.json'
以下は compilerOptions で "target": "esnext" を指定した場合に --listFiles オプションを指定してコンパイルを実行した例です。前述の "target": "es5" の場合より多くの型定義ファイルが対象になっているのが確認できます。